
Disorders of sex development (DSD) represent a group of rare diseases that stem from atypical genetic conditions. Such patients often have impaired health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and psychosocial adaption.
Epilepsy, affecting millions of people globally, is a condition where spontaneous unpredictable seizures occur in the brain. This potentially dangerous condition occurs due to abnormal neuronal network communication in the brain.
Obesity is considered the epidemic of the 21st century. Understanding the aetiology and pathophysiology of obesity should facilitate its prevention, diagnosis and treatment.
Improving the treatments available for diabetic patients and enhancing their health and quality of life represents a major challenge. A European study follows an innovative approach based on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to repair the damage induced by high glucose levels.
When cells grow old or receive stress signals, they undergo a process known as cellular senescence. Understanding the fate of these cells in an organism could help prevent cancer formation and ageing.

Blood insulin levels trigger storage or release of glucose, a simple sugar necessary for all cellular functions but that can cause great damage in excess. Enhanced glucose monitoring during insulin therapy will improve quality of life for diabetics.
RNA therapeutics is gaining ground in the treatment of many diseases. European researchers hope to show it could be a valid intervention for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).

A team of EU-funded researchers have confirmed the correlation between a strong primary care structure and person-focused care in a recent study.

An EU-funded project is building an international consortium to design medical uses for wireless networks and information and communication technologies (ICT).
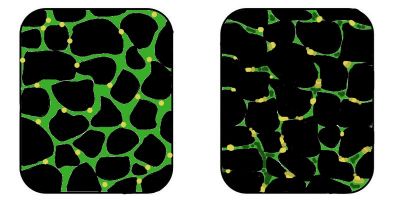
Many degenerative conditions are caused by the accumulation of insoluble amyloid protein aggregates. Finding ways to prevent or reverse this phenomenon is at the forefront of biomedical research and development.
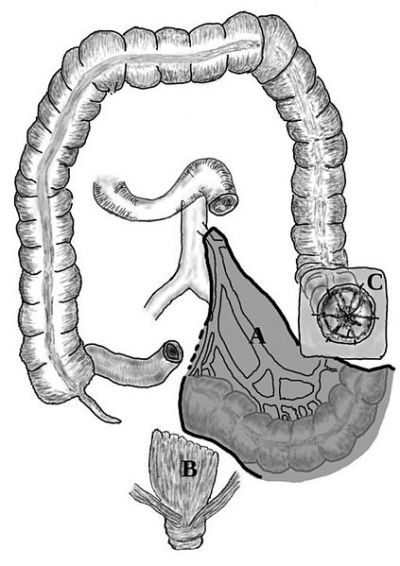
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) involves chronic inflammation of the entire digestive system. European researchers are working to discover biomarkers to improve disease prognosis and clinical management.

Marine organisms being studied by European scientists are a source of novel compounds that could revolutionise the biomedical sector. The first products have been developed for innovative applications.
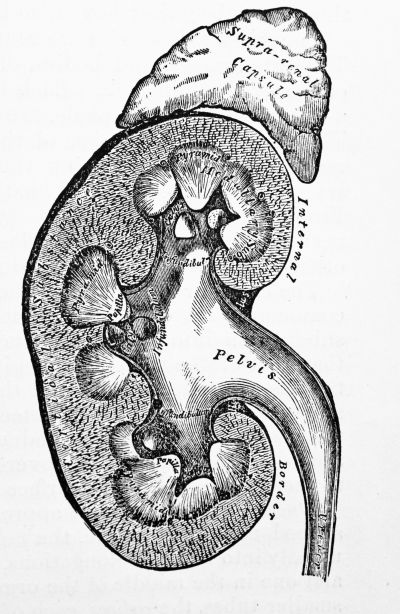
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive loss in renal function over a period of months or years. The early detection of those at risk of developing CKD is necessary as the number of patients is increasing steadily worldwide.
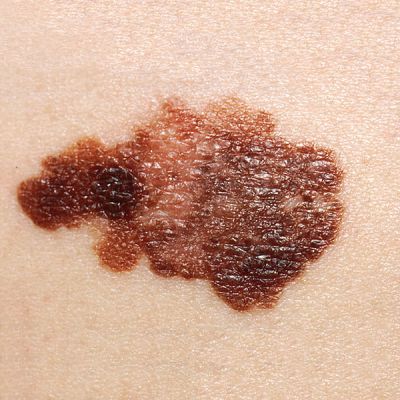
Melanoma constitutes one of the most frequent cancers with a high morbidity rate. Nearly 60 % of cases present with mutations in the BRAF kinase (at position 600), but additional genetic events are thought to be required for malignant transformation.

Unlike magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) that exploits highly abundant protons, an emerging imaging method relies on much less prevalent phosphorous. Scientists exploited new technology that cranks up the signal to detect and classify brain tumours.
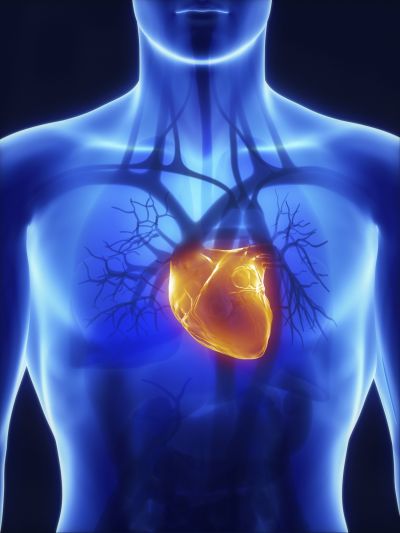
A European study investigated how the inherent capacity of the heart to beat relies on its structure. The generated results and tools should prove useful in the diagnosis of pathological heart conditions.

Sepsis is a major health problem that requires urgent solutions. A European study discovered that certain enzymes released by immune cells could help reduce the extent of inflammation.
The AIDS pandemic still looms over countries in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), urgently requiring innovative treatments. The identification of novel pharmaceutical targets for halting HIV replication will hopefully reduce the magnitude of the problem.
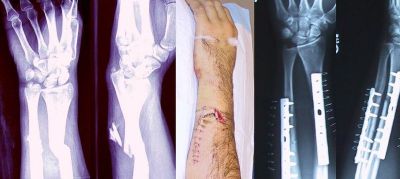
Fixation of broken bones currently relies on mechanical fasteners such as plates, nails and wires. A new bio-inspired hydrogel mimicking a substance produced by marine organisms could be a major advance, particularly for splintered and multiple fractures.
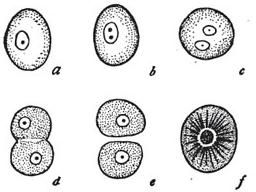
Die Chromosomenzahl in einer Keimzelle einer Art muss immer gleich bleiben. Zu viele Chromosomen verursachen Erkrankungen wie das Down-Syndrom, und zu wenige Chromosomen begünstigen Tumorerkrankungen.

Myelination is crucial for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Study of the mechanisms controlling the synthesis of myelin is essential to identify novel avenues of intervention for demyelinating diseases, such as multiple sclerosis.
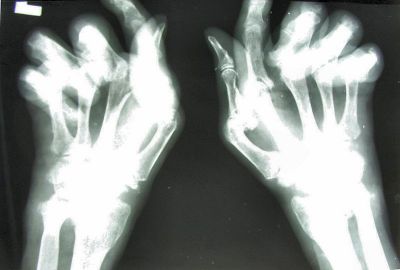
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an incurable autoimmune condition affecting millions of people around the world. EU-funded researchers investigated the gene variants implicated in predisposition to RA.
Congenital syphilis and HIV infections are major causes of infant morbidity and death. The availability of an affordable and user-friendly test that allows same day treatment would save many newborn lives.

Industrialised countries are experiencing a rise in asthma. Understanding the molecular events that culminate in disease pathophysiology is central for designing novel treatments.
Deconvolution of immune responses is central to designing effective immunotherapeutic strategies. A European study focused on specific hepatocyte molecules with a novel role in viral immune responses.
























