
A European project targeted improved health care provision by focusing on the design of catheters. The aim of the study was to develop improved design principles for catheters that reduce clinical complications and patient discomfort.

The cannabinoid system is implicated in many physiological functions of the human body. Cannabinoid receptors present a promising therapeutic target for a number of conditions, including psychological and movement disorders, obesity, neuropathic pain and cancer.

A large multi-disciplinary European consortium is underway to develop a novel drug for preventing blindness in prematurely born infants.

Labour is the largest item of health expenditures and is central to the effectiveness and quality of care delivered.

Gene and cell therapy are emerging as novel alternatives to existing treatments. A European consortium is evaluating the implementation of such innovative approaches for the treatment of epilepsy.
Caesarean section (CS) rates vary considerably throughout Europe. An EU-funded project aims to lower these rates by increasing vaginal birth after caesarean section (VBAC).

Oxidative damage to genetic material affects its integrity and stability, and leads to development of pathologies. Chemical studies of DNA reactivity are fundamentally important as an individual cell can suffer up to 1 million DNA changes per day.
An EU-funded project designed to improve the removal rate of cancerous tumours held its first technical meeting in Brussels recently.
All the functions and dysfunctions in the body are mediated by chemical molecules, billions of them. New experimental techniques have now made it possible to study chemical modifications that play a role in breast cancer.
High blood pressure — hypertension — is a chronic medical condition that increases risk of death from stroke, atherosclerosis and other diseases. The condition results from a complex interaction of genes and environmental factors.

Chronic liver inflammation can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), one of the most common types of liver cancer and the third leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. However, the initial cellular and molecular events that trigger the inflammation are still largely unknown.
Stem cell science and technology hold a great deal of promise for tissue repair and regeneration. A major barrier has been the inability to accurately track cell lineages and to distinguish them from other cell types within the tissue.
The incidence of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), the most common acute leukaemia affecting adults, increases with age. Discovery of novel oncogenes and/or tumour suppressors involved in AML can lead to design of novel therapies for leukaemia treatment.

The RAPTADIAG team has developed a novel diagnostic test for bacterial meningitis which may be used for detecting bacterial pathogens of all kinds.
A significant degree of neuroregeneration occurs in the peripheral nervous system. This process is governed by chemotactic factors secreted from Schwann cells.

Researchers have designed new software tools that will enhance the engineering of drugs.
Cancer represents one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide. Efforts to delineate the mechanisms implicated in cancer onset and progression will have important socioeconomic consequences.

Part of the ageing process is developing low-grade inflammation called inflammaging. To treat this condition, an EU-funded project is working on a dietary approach.

An EU-funded study examined the landscape of personalised health systems (PHSs) to critique the current system and outline means for improvement.
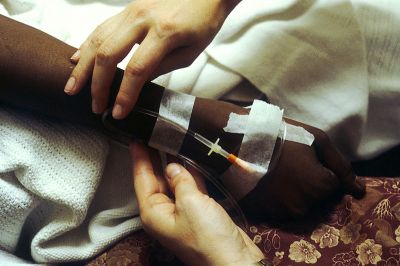
Assessing and predicting the efficacy and toxicity of cancer chemotherapy during the course of treatment would be extremely beneficial. European scientists are very close to accomplishing this with an enzyme detector device.
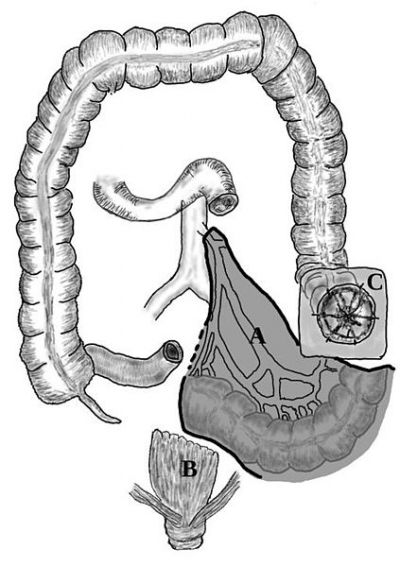
European experts in the field of clinical and experimental immunology are studying NF-kappa-B signalling dynamics and oscillations in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The long-term goal is to identify biomarkers that could be exploited for disease prediction, diagnosis and stratification.
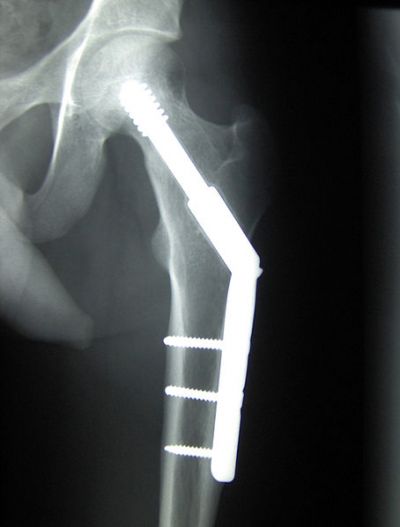
Bioceramics are materials made of alumina or hydroxyapatite, a calcium phosphate mineral. They can be used in the body to replace a functional part like bone material, hips or knees.

Unlike in other tissues, a complex flow of information between brain cells regulates blood supply. Elucidation of the mechanisms coupling brain energy supply to energy use is essential for understanding mechanisms of neuropsychiatric disorders.

Characterising the interaction of bacteria with the human body should lead to a deeper understanding of human biology and improve our overall well-being.
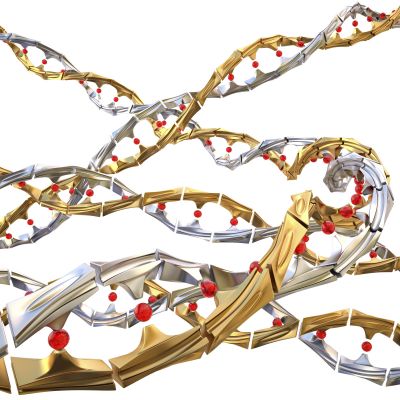
Understanding how cells respond to DNA damage in normal or pathological conditions is of great importance for therapy and cancer.























