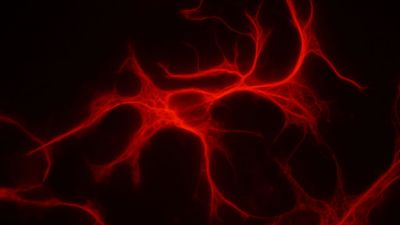
Ageing affects the brain, especially the memory. European researchers have investigated how energy usage in the brain may change as old age approaches.

Chinese and European researchers joined forces to develop novel miniature devices for the biomedical field. Exploiting nano-patterning and microfluidics, the plethora of systems and applications promises to revolutionise analytics and delivery of minute amounts of fluids.

Europäische Forscher entwickelten neuartige Materialien für das Tissue Engineering (Gewebezüchtung). Da sie so konstruiert wurden, dass sie auf spezifische Stimuli, insbesondere bakterielle Infektionen reagieren, dürfte ihr Einsatzspektrum in der Medizin vielfältig sein.

A species of tropical marine cyanobacteria, Lyngbya majuscula, is the source of nearly 300 natural products. Some of them may help in the treatment of cancer, diabetes, HIV and Alzheimer's disease.

Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain among the leading causes of death and suffering in the world. A European study turned to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for solutions.
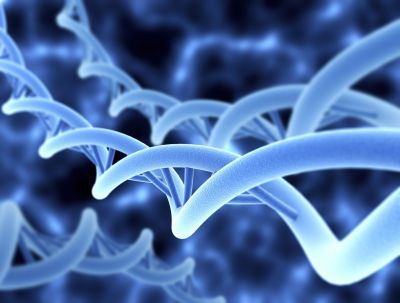
The latest EU research is using magnetic tweezers to investigate unusual DNA structures at the molecular level.
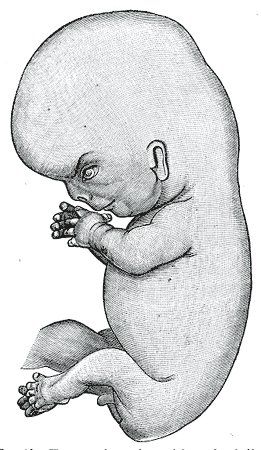
Regulation of gene transcription is critical for development and growth of any organism. EU-funded research has delved into the molecular mechanisms that control the initiation of gene transcription in the developing embryo.

European researchers have uncovered the molecular details of one main mechanism that ensures perfect protein production in the cell.

EU-funded researchers have set out to substitute liquid and freeze-dried vaccines for new, solid state candidates. If successful, the research will enable the large scale production of new virosome-based vaccines with increased stability, longer shelf life and less invasive administration methods.

European researchers are studying epigenetic mutations to understand how gene expression is regulated in health and disease. Epigenetics influences which genes will be expressed by factors other than an individual's DNA sequence.
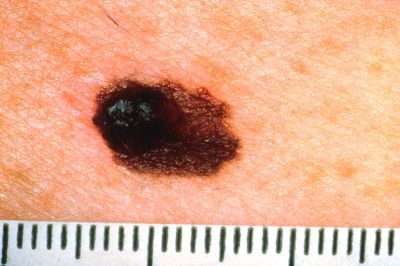
Melanoma is caused by mutations in the melanocytes of the skin. Development of a safe, efficacious melanoma vaccine that could also function in a preventative manner remains a significant challenge.
Understanding how different viruses mediate entry into a cell is central for designing antiviral strategies.
An EU study investigated diabetes self-management in adolescents using a remote e-health interface. The trial found high acceptance of the system among patients, highest among the youngest group, and no real difference between sexes.
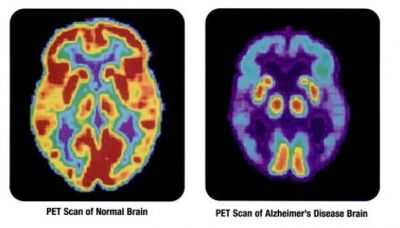
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative condition causing dementia and cognitive impairment. EU-funded researchers performed functional neuroimaging to study alterations in the brain's neuronal networks that correspond to memory impairment.
Understanding why and how people develop rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is central to the development of preventative strategies. Also, the identification of novel biomarkers should help predict disease onset.

Huntington's disease (HD) is a devastating progressive disorder. Delaying disease onset requires novel targeted interventions early on in life.

A new centre at the Medical University of Warsaw (MUW) will address the need for a top-quality experimental oncology platform to support clinical hospitals. Novel research techniques will improve the understanding of carcinogenesis and lead to development of new therapeutic and diagnostic tools.
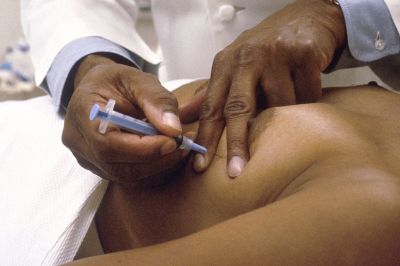
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in men. Realising high-throughput image analysis solutions for prostate cancer should improve the overall accuracy and speed of diagnosis.
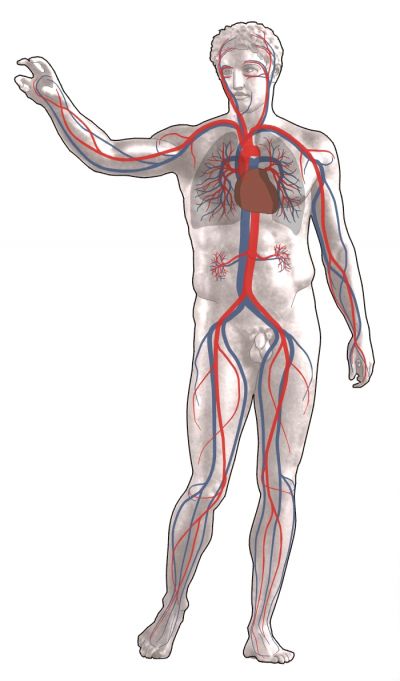
An EU-funded project expanded multidisciplinary networks of players working on research and developing technologies to understand and treat vascular diseases.
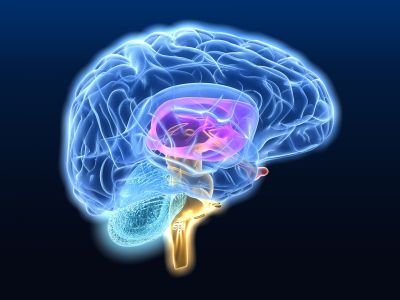
EU-funded scientists have developed a super-resolution optical microscope that produces high-quality images of cells deep within living tissues. This opens the door to the study subcellular brain changes in disease processes or learning.

Joint replacement procedures constitute a medical market calculated in billions per year, increasing with the ageing population. As joint replacements are prone to wear, leading to loss of implant function, it is important to extend their lifetime to avoid repeated surgeries.

Ageing is usually accompanied by multimorbidities, making clinical management a more complex task. The incidence of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) through prescription of potentially inappropriate medications is steadily rising as a result.

Muscles have a unique resistance to cancer and metastasis. Is it possible to learn the resistance mechanism and use it for anticancer therapies?
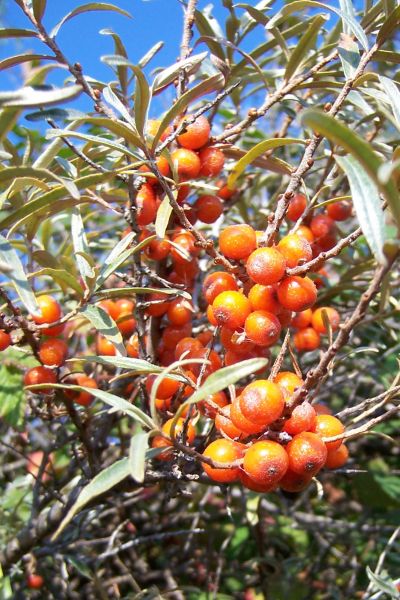

EU scientists have taken steps towards the commercial cultivation of sea-buckthorn, a berry-producing plant with potential medicinal properties.

Positron emission tomography (PET) exploits metabolism of small amounts of a radioactive tracer molecule to evaluate disease or damage. Novel chemicals promise to expand the capabilities of PET from simple glucose to complex molecules like proteins.
























