A European research initiative is continuing development of the skin substitutes Novomaix, denovoDerm and denovoSkin. Clinical studies are testing a one-step surgical procedure.
Stem cells are capable of self-renewal and give rise to specialised cell types. EU research has delved into the biochemical cascades involving signalling proteins and stem cells in the early development of germ layers in the embryo.
A European project is uniting the study sets of the European Biobanking and Biomolecular Resources Research Infrastructure (BBMRI) and other large trials such as the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). The result will be a multidisciplinary, international research initiative on a uniquely massive scale that can deliver an unprecedented amount of data on diseases.

Improving health care in Africa requires policymaking that is based on research evidence that is often inaccessible or incomprehensible for policymakers. An EU-funded project aimed to make research more accessible to policymakers.

An EU project is developing experimental systems and models to replace animals in testing for toxicity effects of new cosmetic and pharmaceutical products.
Positron emission tomography (PET) is the most popular method for verifying that the dose delivered to patients undergoing proton therapy is correct. Now, EU-funded researchers have designed a dedicated PET system that promises to improve the precision of proton dose measurement.
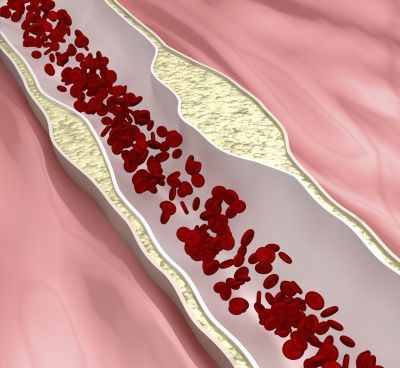
Atherosclerosis is a build-up of plaque on the inner walls of the blood vessels, and complications related to it are a major cause of mortality. Scientists are now conducting the first-ever clinical trials of nanosystems for its imaging, diagnosis and therapy.

Wound healing is a global challenge and different complementary treatment solutions have been developed worldwide. EU funding supported an initiative to bring together wound healing research groups through enhanced communication and knowledge transfer.
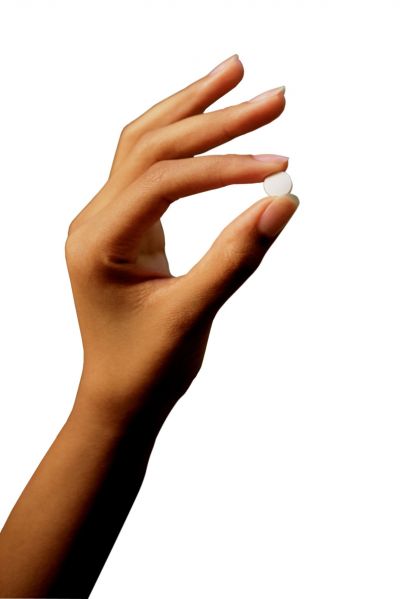
Patients with heart conditions are at high risk of suffering from secondary cardiovascular complications. Treatment generally entails a complex cocktail of medications leading to high costs, inappropriate prescription and poor patient compliance.
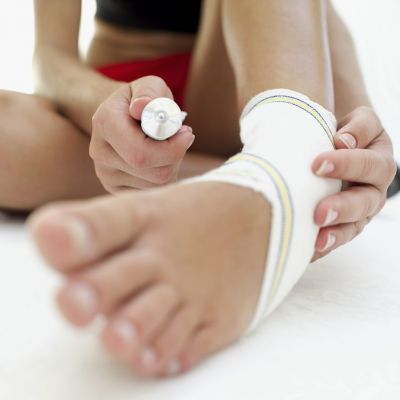
An innovative wound dressing promises to alert for infections and tackle bacteria by locally delivering antimicrobial agents on-demand. This is achieved by integrating natural biological processes with nanotechnology materials.
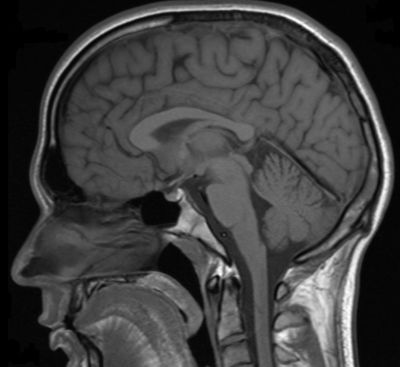
Mapping the complex interaction of brain, spinal cord, blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is required to unveil the dynamics of the brain in health and disease.

Obesity has become a major health issue, and the EU has prioritised the design of healthier foods to control the phenomenon.
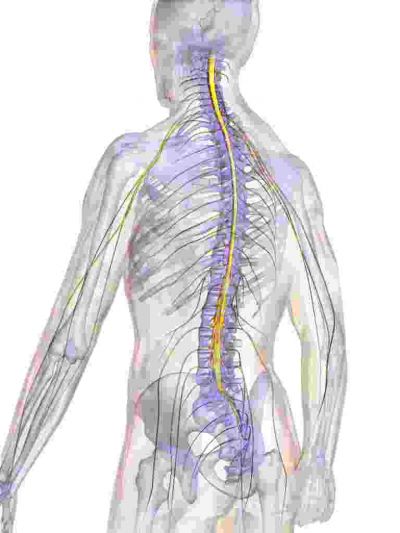
Regenerative medicine is a rapidly evolving field that steps in when traditional medicine fails. With the use of stem cells and growth factors, the regenerative approach promises to heal even spinal cord injuries.

Antimicrobial resistance (AR) is currently responsible for 15 times as many deaths caused by AIDS every year. EU researchers are investigating one of the microbes' genetic vehicles of resistance, the integron.
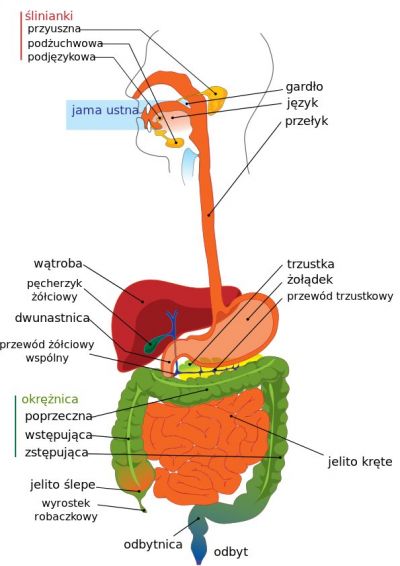
Obesity has become a major health issue, and the EU has prioritised the design of healthier foods to control the phenomenon.

European researchers are using high-throughput technologies to delineate the mechanisms and explore novel therapeutic approaches for rare kidney diseases. The ultimate goal is to improve the dismal prognosis of patient with these disorders.

Onset of glucose intolerance during pregnancy, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), harms some babies and contributes to the type 2 diabetes (T2D) pandemic. A European project is paving the way for a holistic strategy to prevent GDM.
Cancer ranks amongst the biggest causes of mortality worldwide. There is an ongoing need to understand the underlying mechanisms of cancer onset, progression and metastasis.
An EU team has contributed to efforts aimed at reducing health care costs by helping to prevent mental decline in elderly citizens. To that group, the project also communicated the benefits of EU health research via a collaborative process and by engaging media such as films.
Several neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson's disease, are associated with dysfunctions of the dopamine system. Understanding dopamine synthesis regulation will facilitate exploration of new therapeutic options for such diseases, affecting millions of people worldwide.

Elucidating how the immune system develops in humans is central to treating or preventing infections in newborn babies.

An EU project has improved on measures of air pollution associated with transport, allowing a more in-depth understanding of its effects on human health.
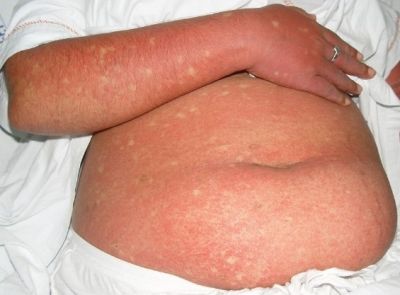
Around 400 million cases of dengue fever worldwide highlight the need for better disease management as well as effective transmission control and therapy. EU funding is supporting scientists in this endeavour.
Age-related disorders are on the rise with increasing life expectancy. Understanding the pathology and the underlying mechanisms of these conditions is crucial for finding effective therapies.

Mental fatigue experienced during neuromuscular rehabilitation is currently detected using electroencephalography (EEG)-based systems. A first, researchers successfully combined video monitoring and EEG to quantify mental fatigue.
























