
Therapeutic antibodies represent one of the fastest growing areas in pharmaceutical biotechnology. Pioneers in the field joined forces to comprehensively study and further optimise these promising therapeutic agents.
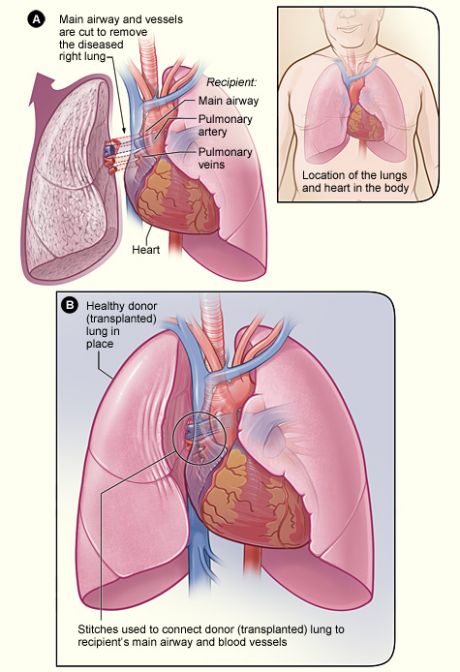
European scientists developed a novel clinical mathematical tool capable of interpreting a particular molecular signature and predicting the outcome of lung transplantation (LT).
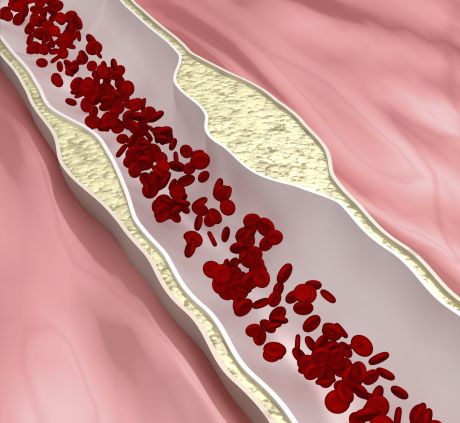
The leading cause of death, cardiovascular disease is a late manifestation of atherosclerosis. An EU study explored biomarkers for subclinical atherosclerosis to empower the development of early preventive and treatment strategies.

Osteoarthritis, a leading cause of disability in the developed world, ultimately necessitates use of joint replacements. These implants have limited life, and issues with implant fixation and loosening limit their utility.
Sudden cardiac death (SCD), typically caused by arrhythmias, can be averted with implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs). An EU-funded project studied interactions of antiarrhythmic drugs with ICD therapy and ischaemia.
A European consortium is testing the efficacy of a cell therapy approach for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
Five European studies are working to revolutionise screening and treatment practices in healthcare settings and primary care to minimise transmission of drug-resistant bacteria.

Understanding how type I interferons function is central to predicting unwanted responses during therapy.

European researchers are investigating an innovative therapeutic approach based on the conversion of endothelial cells to another cell type.
Nanotechnology is becoming an indispensable component of many scientific sectors. In medicine, nanotechnology has the capacity to drastically change how we diagnose and treat may diseases, including cancer.

Long-term administration of nicotine results in neural and behavioural plasticity, responsible for relapses even after long-term abstinence. An EU study investigated genetic mechanisms of this behaviour using a model organism.
A recent EU-funded project has developed microscopic physical markings for pharmaceutical and medical products to prevent counterfeiting.
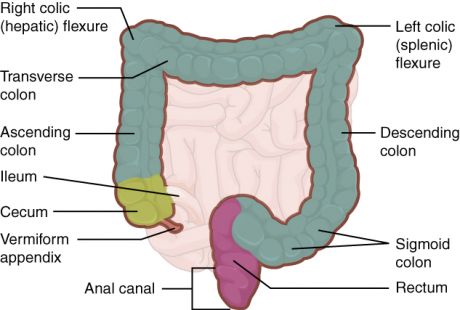
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers in both men and women. An EU project investigated potential biomarkers for CRC risk prediction.

To address rising concerns regarding a new class of anti-inflammatory medications used for children, an international study investigated their side-effects over time.
Intervertebral disc (IVD) pathology is one of the most important topics of regenerative medicine. An EU project is investigating the role of hypoxic signalling in the pathological changes of the cartilage and IVD tissues.

Modern lifestyle has dramatically changed the circadian rhythm of life of European citizens. A new study is looking at how such changes may affect endocrine and metabolic processes and lead to the development of type 2 diabetes (T2D).

Hadron therapy uses beams of charged particles (ions) to destroy tumour cells. The ENVISION project was dedicated to providing real-time imaging tools to ensure precise and complete elimination of tumours.

The adage 'we are what we eat' applies to our long-term health and well-being. Predisposition to obesity and metabolic disorders can be linked to diet and lifestyle right from our time in the womb.

In the last days of life, cancer patients need a particular kind of care. An EU-funded project worked to optimise research for the care of this population.
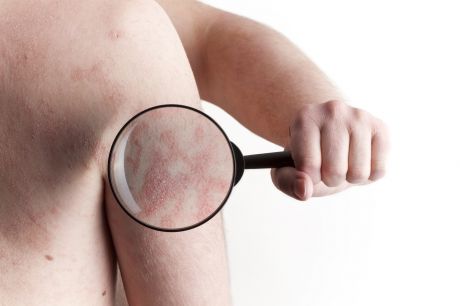
European researchers worked to unveil the molecular aetiology of inflammation-related skin conditions such as psoriasis. The findings of the study have the potential to lead to novel treatments.
Cell to cell adhesion is critical for the development and integrity of solid tissues. EU researchers investigated a family of molecules, the cadherins, which play a key role in ensuring that cells stick together to form stable tissues with well-defined mechanical properties.

Scientists have found numerous ligands of a membrane-bound protein implicated in an unusual array of pathologies from neurotoxicity to prostate cancer. The ligands will help unravel diverse functions and develop targeted therapies.
Understanding how influenza virus evolves within its host is central to predicting the emergence and spread of new strains.
Sudden cardiac death (SCD) due to cardiovascular disease is the number one killer globally. EU-funded researchers worked on understanding the mechanisms leading to SCDs.
A European study pursued a new avenue in the design of drugs against malaria: it explored gene translation in the parasite Plasmodium falciparum as the target.
























