
Researchers have discovered how star-shaped cells called astrocytes control brain development and connect neural circuits, taking a step towards treating neurodegenerative disorders.

Pancreatic cancer is the fourth cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Current therapies are not effective, thereby necessitating targeted approaches against implicating molecules.

Despite being an ancient infectious disease, the elusive cure for tuberculosis remains one of the main priorities of the scientific community worldwide.

A European study developed an interesting strategy for treating cancer by inducing cancer stem cells to differentiate.

Targeted drug delivery to desired cell types increases therapeutic efficiency and minimises undesired side-effects. A European research project worked on developing a novel concept for targeted drug delivery into neuronal and cancer cells.

Calcium signalling is important for various functions in virtually all cells. In T lymphocytes of the immune system calcium is necessary for gene expression regulation.
A new automated drug safety surveillance tool may help identify adverse drug reactions not detected in pre-market clinical trials using multiple data sources.

Our perception of time, space and other people defines our mental orientation. European scientists provided unprecedented evidence on the role of orientation in neuropsychiatric disorders.
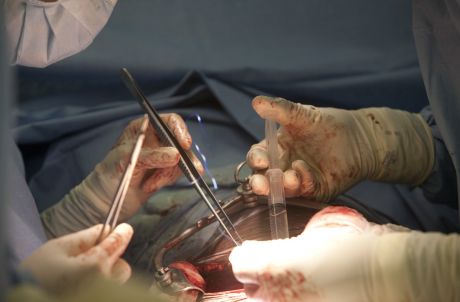
Delayed graft function (DGF) a complication of early graft dysfunction often follows organ transplantation. Targeting this condition, a novel antibody treatment may prevent loss of graft function and ultimately transplant failure.
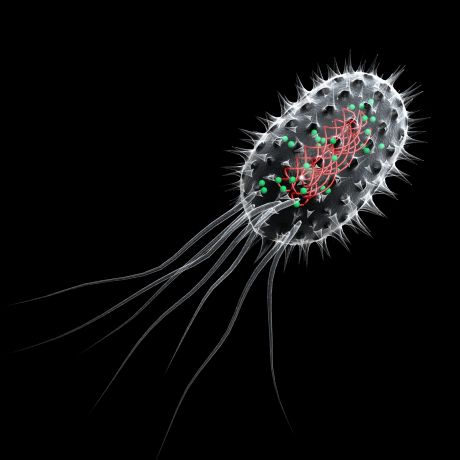
Over the years, research in the area of drug delivery has come a long way. The STOPP VEHICLES study exploited the path travelled by bacterial toxins to deliver drugs within cells.
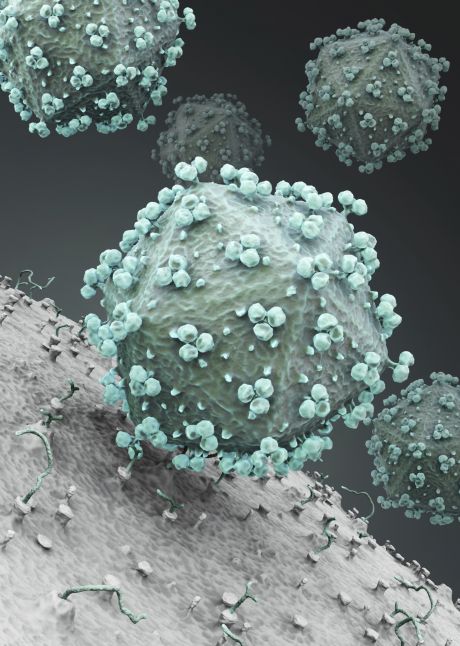
Despite advances in anti-retroviral therapy, HIV infection remains one of the biggest medical challenges so far. Understanding virus-host interactions is fundamental to the design of new anti-HIV drugs.

Rising obesity, addiction and stress levels are a major public health concern. An EU initiative that investigated the neurobiology of stress, addiction and eating behaviour provided fresh insight.

Health claims made by food manufacturers may soon be substantiated by biomarkers that measure how food compounds affect healthy and unhealthy individuals.
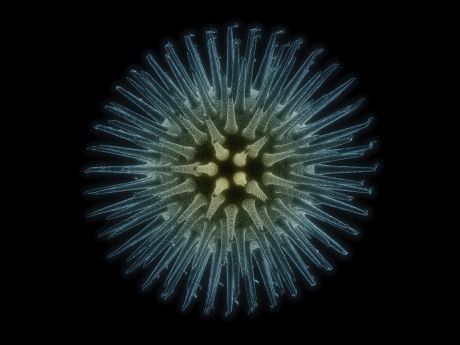
EU funding is continuing to work on therapies to tackle emerging and neglected RNA viruses. Diseases include the newly emerging Zika virus, Ebola virus, human MERS and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS).
Cancer remains the second most common cause of death in the EU despite recent significant advances. The development of more effective targeted therapies could dramatically improve the way we treat the disease.
Anti-cancer research never sleeps. Scientists are always in the process of discovering and developing new, more specific and less toxic drugs.
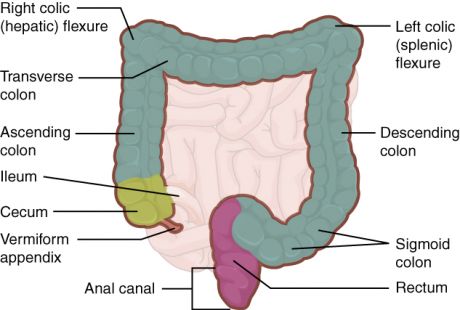
A major limitation of targeted therapies for colorectal cancer is the emergence of secondary resistance. European scientists are prospectively screening for genes that mediate such acquired resistance, aiming to identify specific drug resistance biomarkers.
European scientists have created the NaNose, a device that can detect lung cancer from the breath of a patient in less than 10 minutes.
Understanding the process of cardiac regeneration is of fundamental importance for the design of regenerative therapies. Many chronic cardiomyopathies and myocardial infarction lead to cardiac muscle death. If apoptotic cardiomyocytes do not get replaced this can lead to severe deficiencies in cardiac pump function.

Does work or the lack thereof affect health? An EU initiative shed light on the consequences of work on health.

Researchers have created molecules whose shape and surface chemistry mimic that of double helical DNA

Researchers have studied data from the International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) and found that insertions of genes or parts of genes are commonplace in cancer genomes.
Scientists have developed a rapid new method to analyse blood for signs of cardiovascular disease.

Patients with diabetes are living longer. Primary care is targeting the increased number of patients with associated kidney disease as well as cardiovascular disease (CVD).

Advances in modern medicine substantially increase life expectancy for the EU's ageing population, saving lives of patients with previously fatal diseases. As a consequence, there is an increased number of patients with chronic medical conditions.






















