Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease associated with increased levels of immunoglobulin D (IgD). Understanding the connection between the two will lead to improved therapies for SLE.
European researchers joined forces to unravel the function of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in breast cancer. The generated knowledge will drive the future of translational medicine.
According to the World Health Organisation, there are approximately 3 million people worldwide, who are obese or suffer from diabetes. Finding a cure necessitates going back to the drawing board and investigating cell biology.
European researchers set out to dissect the process of protein aggregation, a hallmark of many degenerative disorders. Identification of the key players in amyloid formation may lead to novel therapeutic targets.

Characterising the interaction of bacteria with the human body should lead to a deeper understanding of human biology and disease and so help improve our overall well-being.
European researchers investigated the role of host proteins in Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. The findings may serve as the basis for innovative new therapies.
Through manipulation of epigenetic modifications, scientists hope to establish a new line of anti-cancer therapies. However, the emergence of therapy resistance necessitates investigation into the underlying mechanism.
Even normal ageing causes a decline of memory functioning is an indisputable fact. An EU-funded project has evaluated young and old to get information for feeding more reliable computational models of ageing and its effects.

An EU-funded project is investigating the benefits of palmitoleate (PAO) for the treatment of atherosclerosis and inflammation. Macadamia nuts and sea buckthorn are particularly rich in this omega-7 fatty acid – vegetarians can also benefit.

Somatic stem cells are present in most tissues and contribute to tissue homeostasis by replenishing short-lived cells. Understanding how this occurs is key for regenerative medicine.
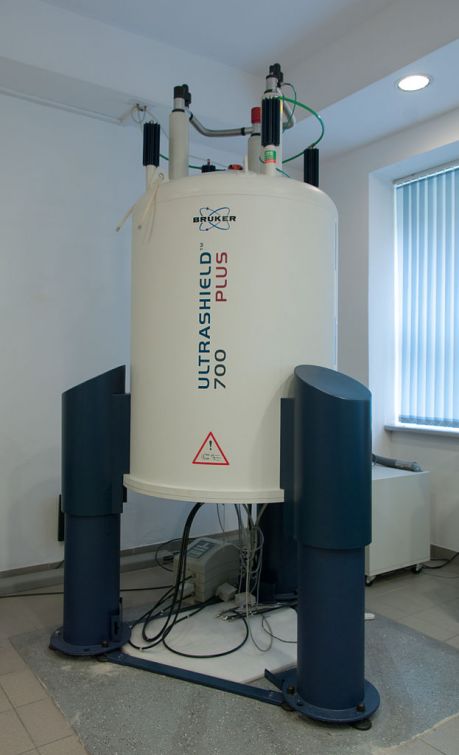

Determining the structure of biological components is key to understanding biochemical pathways in living tissue. EU funding supported the development of European nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) infrastructures for biological applications.
The annual healthcare expenditure in Europe arising from neonatal medical conditions with an acute threat to the brain is currently billions of euros. However, current practice and equipment in this field are far from optimal.
The inflammasome is a biochemical pathway and a key innate element in fighting infections. The downside is that its action is involved in some inflammatory syndromes.
Obesity and diabetes both happen as a result of malfunction of glucose balance regulation. EU researchers have targeted what may be viewed as the crux of the problem, nerve cells that respond as glucose levels rise.

Scientists have gained insight into the role of sleep in memory formation as well as developing targets for sleep disorder therapies. It seems that sleep disturbance goes beyond nodding off in that important meeting.

Antibiotic resistance is one of the major health challenges of the 21st century that has yet to be addressed. Concerted efforts are thus necessary to design and develop novel anti-bacterial drugs.
Collaboration between a range of professionals and healthcare organisations is necessary for ongoing care of the infirm and elderly. This project identified quality indicators (QIs) specifically to improve the care of cancer and dementia patients in Europe.
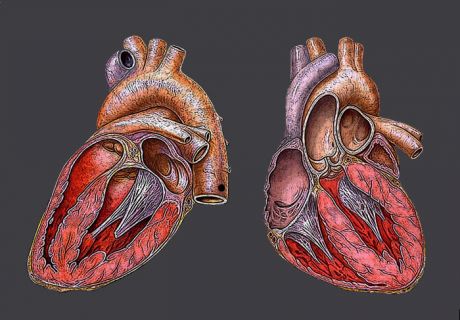
Heart failure is a leading cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality worldwide. Understanding the mechanisms responsible for cardiac dysfunction will help design novel therapies.
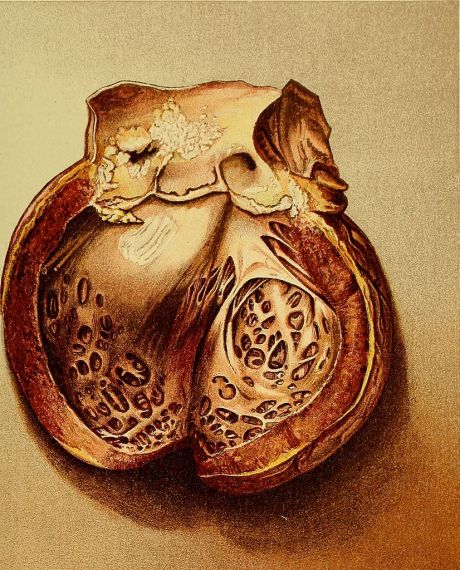
European researchers are investigating a serious morbidity of inflammation, arterial calcification. Their findings could help reduce the incidence of diseases that involve artery blockade such as cardiovascular disease.

Metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity are reaching epidemic proportions, particularly in developed countries. EU-funded researchers are investigating the role of the retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) receptor in regulating metabolism.
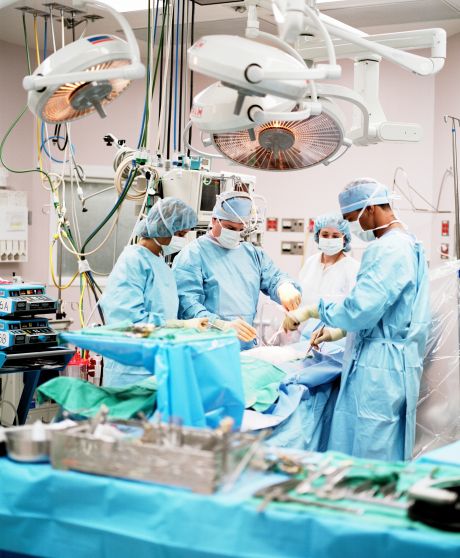
EU funding supported an exciting venture that has developed smart magnetic solutions to safely and cost-effectively perform minimally invasive surgery. This could reduce health care costs and speed up patient recovery.

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammation of the gut. A European consortium is following a systems medicine approach for disease management.
Understanding how drugs can induce allergic responses is central to designing diagnostic tests and taking prompt action.
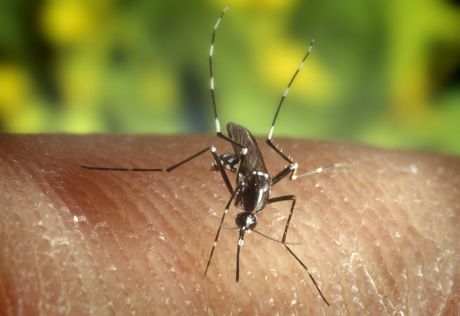
An international alliance has joined forces to integrate research efforts worldwide towards providing a cure for malaria.
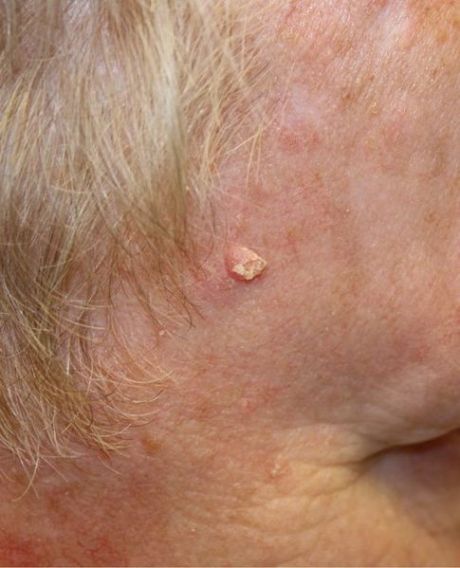
A European consortium is working on delivering an immune-modulating agent at the tumour site. The results from the clinical trial for Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) treatment could also be used for treating other types of cancer.
























