
Neurons in our brain are crucial for information processing but their study is a complex endeavour. EU funded researchers developed optogenetic tools to overcome associated technical issues.
European researchers worked on novel anti-retroviral drugs against HIV. Their deliverables offer enhanced protection against virus transmission.

Arrhythmias are abnormal cardiac electrical rhythms that are difficult to predict and potentially life threatening. Current therapies include antiarrhythmic drugs and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) devices that have limited efficacy.
Despite numerous successes, vaccine development for many diseases poses a great challenge. Ongoing efforts to improve vaccine effectiveness include the optimisation of adjuvant substances.
Nanoparticles are increasingly being used in medicine. Their exploitation as anti-cancer therapeutics requires that they are homogeneously delivered to their target.
Atherosclerosis is a major cause of death in developed countries. To understand disease pathobiology and the underlying biological processes, a European study developed an integrated computational model framework.

Development of a prophylactic vaccine that stops HIV infection remains a high priority. A novel safe and effective approach to induce immune response against HIV is in the pipeline thanks to EU research.

Recent advances in DNA and RNA sequencing have transformed the field of genomics, making it possible to generate large amounts of data rapidly and at low cost. Now, EU-funded researchers have developed the statistical tools needed for the analysis of hundreds of gigabytes of data produced in each single sequencing run.

Insight into the early processes underlying chronic inflammation could aid in understanding the onset and progression of allergic or autoimmune diseases.

A European network investigated Notch signalling in health and disease. Apart from mechanistic insight into the pathway, the results of the study carry significant translational potential.

Mitochondrial DNA deletions are emerging as the underlying cause in many diseases. A European study will unveil how mitochondrial DNA gets damaged and investigate the mechanisms for repair or prevention

New molecular analysis technologies have facilitated the identification of novel protein networks as therapeutic targets. Combining systems biology and animal modelling, a European study has investigated cilia function in health and disease to discover novel therapies.

European researchers investigated the complex process of cancer metastasis, paying particular attention to the role of macrophages.

A large European network set out to comprehend the emergence and spread of vector-borne diseases (VBD). Their results have important health consequences.

The next revolution in medicine entails a shift towards predictive diagnostics and individualised therapies. In this context, European researchers identified novel targets for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases (CVD).
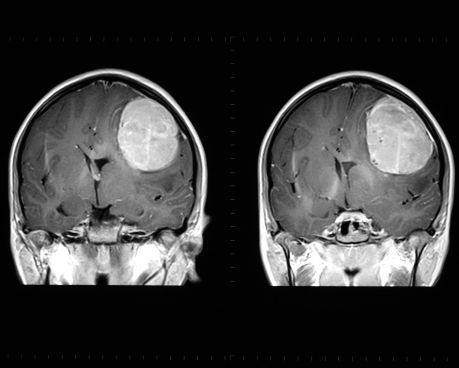
Clinical management of a number of cancers relies on prompt and accurate diagnosis. European researchers worked towards this goal by developing novel diagnostic tools.

An EU research project has investigated how the genomes of cells in the body, somatic cells, become varied and form a mosaic. One source is the action of jumping genes or transposable elements (TEs).
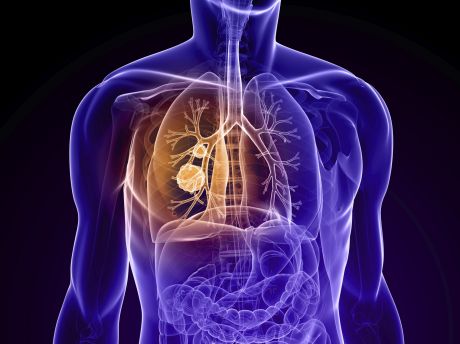
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a major health issue with hundreds of thousands of deaths each year. New, targeted therapies are urgently required to improve the dismal statistics of this disease.
Although millions of different species of fungi exist, only a few are capable of causing allergies or serious infections in humans and animals. Traditional reductionist approaches of the past have not been sufficient to address the new challenges in the pathogenesis of fungal diseases.
Lymphocytes are key effector cells of our immune system. Understanding the molecular mechanisms that drive their development could help understand many immune-related diseases.
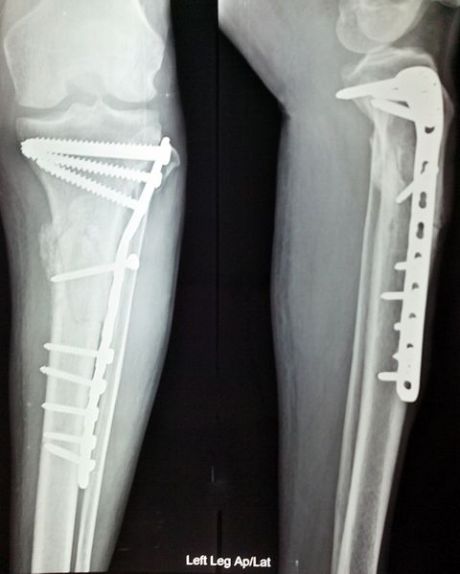
Young researchers across the EU have developed new titanium (Ti)-based implant technology as part of an international training network.
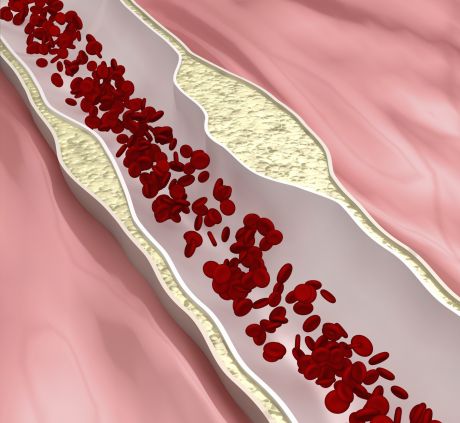
European researchers investigated how regulators of gene expression might affect the arteriosclerotic degeneration of blood vessel walls. Their findings, apart from facilitating prompt diagnosis, could have therapeutic relevance as well.
Certain diseases carry with them odours that physicians use for diagnosis. EU-funded researchers explored the use of laser absorption spectroscopy (LAS) as a breath sensor for detecting cystic fibrosis (CF).
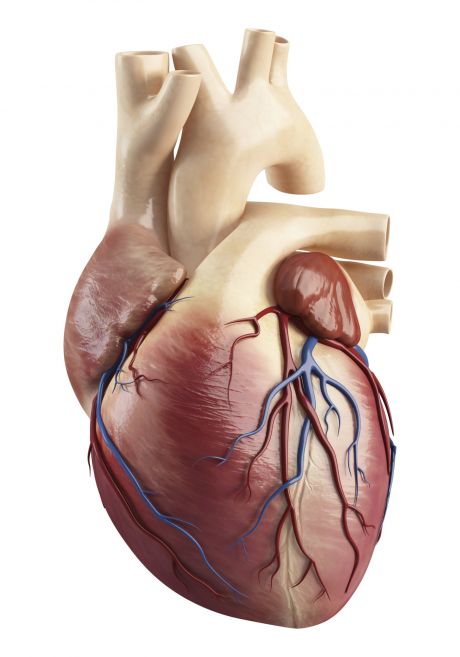
Cardiac diseases are one of the top global killers. Comprehending the function of cardiac muscle components should help resolve dysfunction through novel interventions.

European researchers developed a series of innovative antibody-like tools that allowed them to study breast cancer and discover new biomarkers.
























