
Evidence-based guidelines are helping the policy and practice of a comprehensive approach to improve health literacy of the ageing population in the EU.
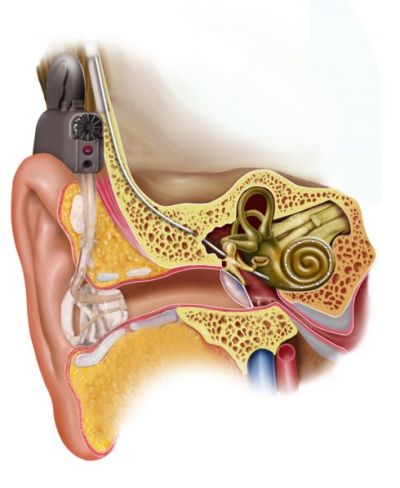
In Europe alone, over 80 million people suffer from progressively worsening severe hearing loss. EU-funded researchers are developing regenerative cochlear implants (CIs) to prevent further degeneration and improve hearing quality.

Out-of-pocket health care expenditure in low-income countries like India causes further impoverishment, leading to limited health care uptake. Researchers implemented three community-based health insurance (CBHI) schemes to resolve this.

The European population is increasingly composed of a higher proportion of elderly people. Resolving cognitive decline has become crucial with about 50 % of adults aged over 85 suffering from neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's (AD).

The fourth leading cause of death, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) afflicts over 300 million people and is a huge socioeconomic burden. Telemedicine-based care models could alleviate the impact of such diseases.
Diabetes represents a major medical issue as it damages the cardiovascular system, causing disease. A European study set out to understand how diabetes alters the pathophysiology of blood vessels
Delayed graft function (DGF) is a condition that often follows organ transplantation. A novel antibody treatment may prevent graft rejection following transplantation by targeting DGF.

A European consortium has developed a point-of-use test (POUT) analysis system that can be used for human health, agri-food and veterinary applications; all modifiable at the point of manufacture. A fibre-based paper or card substrate has provided the innovative basis for low-cost yet rapid diagnostics.
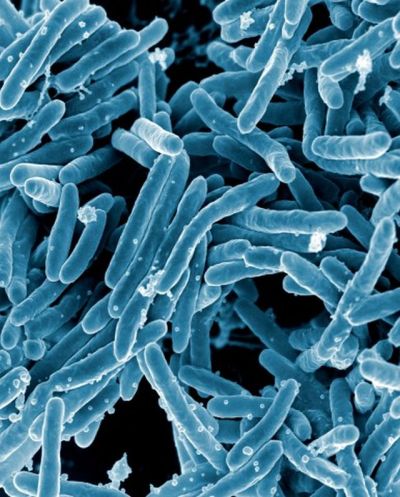
Tuberculosis (TB) is a re-emerging global health threat affecting one third of the world population. Understanding the mechanisms of pathogenesis, virulence and persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTb) infection will enable addressing it in a more efficient manner.
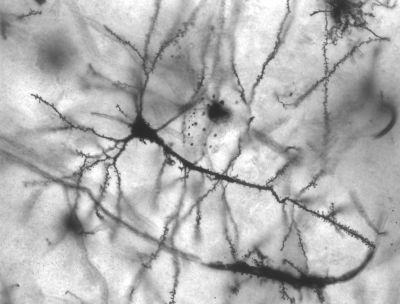
European researchers investigated the structure of neurons in normal and abnormal conditions. Their work focused on the localisation and modification of ion channels, which are vital for proper signal transmission.
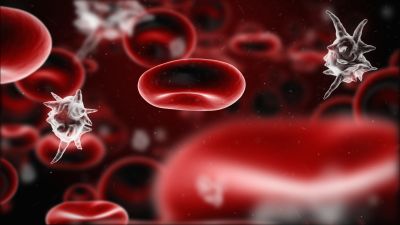
Sepsis causes annually up to 135 000 deaths in Europe, and rapid diagnosis is the key to improved survival. Combining pathogen collection from whole blood using ultrasonic sound waves and photoluminescent DNA detection technology promises to make this a reality.

Manipulation of the immune system to tackle diseases requires a deep understanding of its biology. In this context, European researchers studied a newly identified population of immune cells and how it functions within the immune system.

Functionalised nanoparticles are paving the way to targeted drug delivery and imaging applications. A novel synthesis route to achieve particles activated by harmless infrared (IR) radiation supports effective photodynamic therapy of cancer.

The successful regulation of emotion regulation is vital to mental health and well-being. EU-funded research has advanced knowledge on one factor that may promote successful emotion regulation: the belief that emotion regulation is indeed possible.
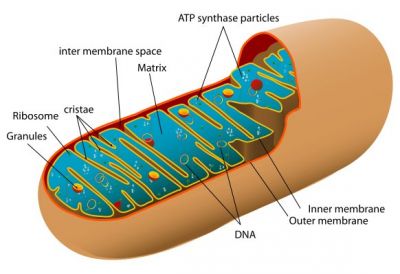
Understanding the molecular aetiology of disease sometimes means having to go deep into the cell's organelles and their constituents. A European study researched mitochondrial DNA to comprehend what goes wrong in various disorders.
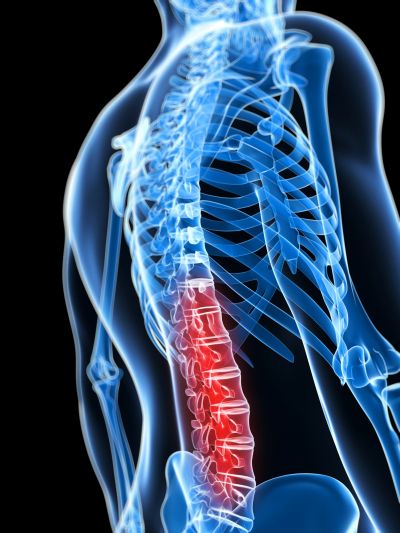
Nearly one third of people show intervertebral disc degeneration to some degree by the time they are 35 and most do by the age of 60. A new biomechanical model of the cushions between the bony vertebrae could lead to new therapies and relief for millions.
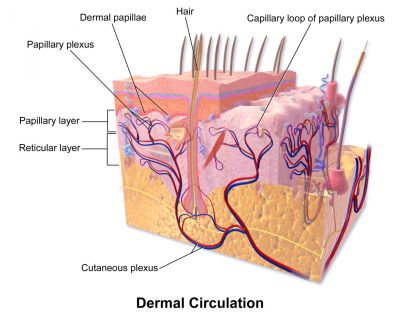
European researchers are working to understand the pathways that govern skin homeostasis and repair. This information is vital for treating skin injuries.

Macular and retinal degeneration commonly cause blindness in aged people, posing considerable socioeconomic burden on society. A four-year study focused on understanding the mechanism of healthy retinal homeostasis.

A European consortium set out to dissect the molecular aetiology of Huntington's disease (HD). Their findings should lead to more specific and targeted therapies.
In cases where the body's capacity for bone healing is insufficient, bone grafts have been the most common solution. Thanks to an improved biomimetic scaffold with low doses of growth factors, patients can soon expect better treatment at lower cost.
The prevalence of metabolic disorders and their co-morbidities is increasing at an alarming rate. To improve diagnosis and therapy, new biomarkers are urgently needed.
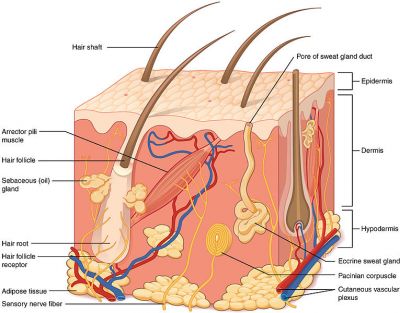
European researchers are working to understand the pathways that govern skin homeostasis and repair. This information is vital for treating skin injuries.
In many instances, herbs are used as medicinal products to treat or alleviate the symptoms of many conditions. A European study discovered that certain fruits have anti-diabetic and anti-hypertensive properties.

Cardiovascular disease is one of the biggest medical challenges today. European scientists developed novel innovative foods based on the legume lupin to join the battle for cardiovascular disease prevention.
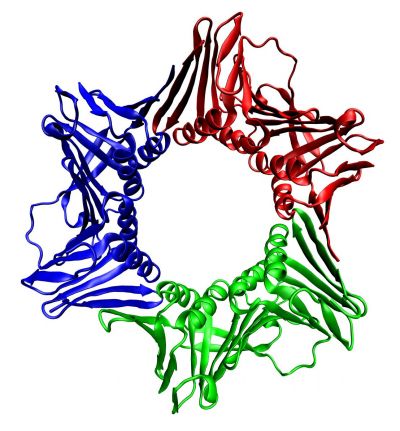
Proteins assume a complex 3D structure after manufacture in order to achieve their final functionality. Advanced spectroscopic methods shed light on cellular quality control mechanisms with atomic resolution.
























