
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide and the technology for rapid diagnosis and treatment necessary to improve prognoses is lacking. A novel point-of-care diagnostic helmet is set to change that.
Our bodies are capable of forming new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis. Studying the molecular triggers of this phenomenon could lead to the design of novel therapeutic interventions.

Drug resistance is one of the most important factors in malaria treatment failure, often with deadly consequences. A pioneering cell phone-type device that analyses infection and malarial mutations with a finger prick could save billions of lives.
Antibiotic misuse triggers the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria. Understanding the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon should help develop appropriate measures.

The chronic shortage of effective health workers is a key obstacle to improving health and saving lives in Africa. An EU initiative has set out to enhance health services (HSs) in sub-Saharan Africa by improving the performance of the existing health workforce.
Understanding how tumours spread and generate metastases is central to therapy. A large consortium of European scientists focused on hypoxia for answers.

Proprioception refers to our ability to sense the position and movement of our limbs through complex signal integration in the brain. EU-funded researchers investigated the inner workings of the brain during this process.
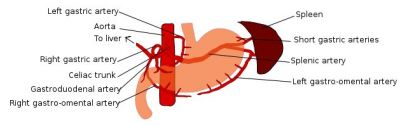
European researchers developed a novel in vitro culture system that closely mimics the structure of the human stomach. Using this model, it is now feasible to study host-microbe interactions.
Anaemia, associated with chronic kidney disease, is a serious complication affecting millions of European patients. Using anticalin scaffolds, an EU-funded study aims to develop a novel therapy for tackling anaemia.

Vaccination has long been at the forefront of tackling infectious diseases. Ongoing efforts aim to enhance the performance of existing vaccines and develop new ones against novel targets.
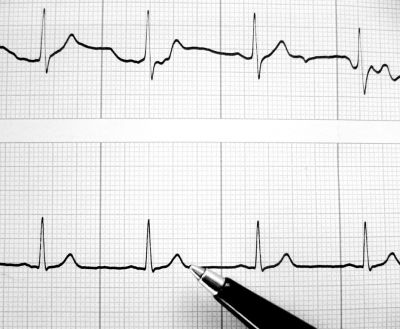
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a most common cause of heart arrhythmia and affects up to 2 % of the European population. Developing earlier diagnosis and new therapeutic methods to address AF will save billions in health care costs.
Biomedical imaging has had major impact on the detection, diagnosis and treatment of cancer, significantly improving outcomes for millions. A novel multimodal system gains strength in numbers for even higher specificity of tumour differentiation.
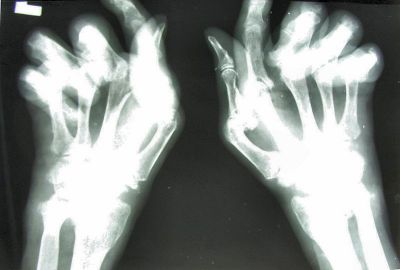
EU scientists are developing a new treatment for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) based on the intravenous administration of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from fat tissue. Initial results showed that MSC therapy lead to a promising clinical outcome in treated patients
Recent studies highlighted the role of metabolism in a number of human malignancies. Pyruvate is the key player in cellular metabolism in mitochondria and its regulation might be altered in cancer cells.
More and more, medicine depends on materials science for the development of innovative materials used in various applications. Nanotechnology is rapidly entering the field as the major constituent of materials used in tissue engineering.

Due to our ever changing environment and habits, exposure to environmental contaminants is growing increasingly complex, but the health impact of environmental hazards remains poorly characterized. Prospective studies focusing on periods of high susceptibility, such as early life, should help predict individual disease risks related to the environment.
Childhood interstitial lung disease (chILD) refers to a group of over 100 rare lung diseases that affect babies, children and teenagers. Symptoms include chronic cough, shortness of breath and rapid breathing.
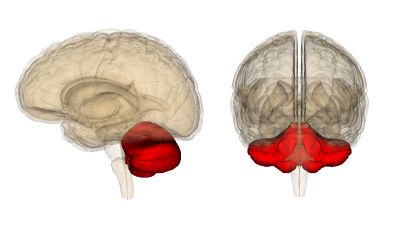
A European network of academia and industry set out to perform a multidisciplinary study of the cerebellum. The generated information brings us a step closer to comprehending the function of this complex organ.
Neuroimaging probes the mysteries of the brain and offers a first-hand look at the human body's most important and complex organ. EU researchers joined forces to advance the know-how of this relatively new and constantly evolving discipline.
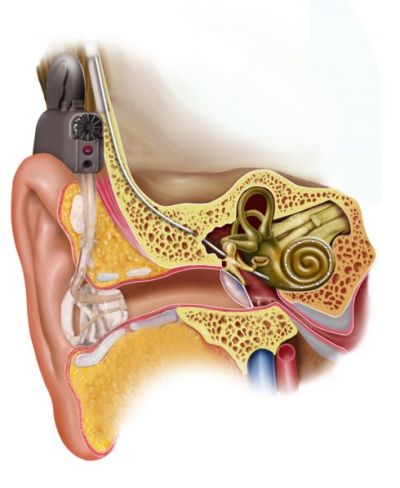
In Europe alone, over 80 million people suffer from progressively worsening severe hearing loss. EU-funded researchers are developing regenerative cochlear implants (CIs) to prevent further degeneration and improve hearing quality.

The European population is increasingly composed of a higher proportion of elderly people. Resolving cognitive decline has become crucial with about 50 % of adults aged over 85 suffering from neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's (AD).
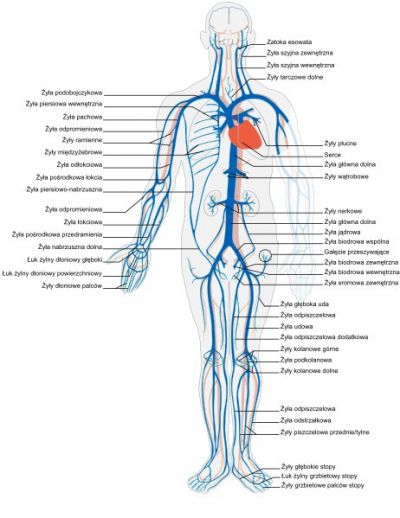
Diabetes represents a major medical issue as it damages the cardiovascular system, causing disease. A European study set out to understand how diabetes alters the pathophysiology of blood vessels

A European consortium has developed a point-of-use test (POUT) analysis system that can be used for human health, agri-food and veterinary applications; all modifiable at the point of manufacture. A fibre-based paper or card substrate has provided the innovative basis for low-cost yet rapid diagnostics.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a re-emerging global health threat affecting one third of the world population. Understanding the mechanisms of pathogenesis, virulence and persistence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTb) infection will enable addressing it in a more efficient manner.
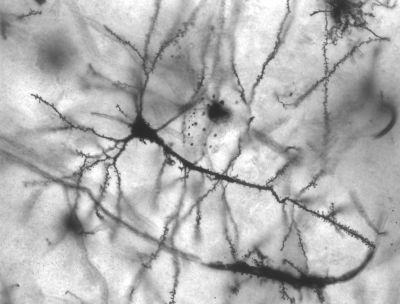
European researchers investigated the structure of neurons in normal and abnormal conditions. Their work focused on the localisation and modification of ion channels, which are vital for proper signal transmission.
























