
Long-term administration of nicotine results in neural and behavioural plasticity, responsible for relapses even after long-term abstinence. An EU study investigated genetic mechanisms of this behaviour using a model organism.
A recent EU-funded project has developed microscopic physical markings for pharmaceutical and medical products to prevent counterfeiting.
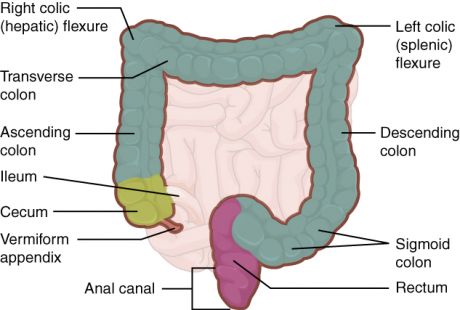
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers in both men and women. An EU project investigated potential biomarkers for CRC risk prediction.

To address rising concerns regarding a new class of anti-inflammatory medications used for children, an international study investigated their side-effects over time.
Intervertebral disc (IVD) pathology is one of the most important topics of regenerative medicine. An EU project is investigating the role of hypoxic signalling in the pathological changes of the cartilage and IVD tissues.

Modern lifestyle has dramatically changed the circadian rhythm of life of European citizens. A new study is looking at how such changes may affect endocrine and metabolic processes and lead to the development of type 2 diabetes (T2D).

Hadron therapy uses beams of charged particles (ions) to destroy tumour cells. The ENVISION project was dedicated to providing real-time imaging tools to ensure precise and complete elimination of tumours.

The adage 'we are what we eat' applies to our long-term health and well-being. Predisposition to obesity and metabolic disorders can be linked to diet and lifestyle right from our time in the womb.

In the last days of life, cancer patients need a particular kind of care. An EU-funded project worked to optimise research for the care of this population.
European researchers worked to unveil the molecular aetiology of inflammation-related skin conditions such as psoriasis. The findings of the study have the potential to lead to novel treatments.
Cell to cell adhesion is critical for the development and integrity of solid tissues. EU researchers investigated a family of molecules, the cadherins, which play a key role in ensuring that cells stick together to form stable tissues with well-defined mechanical properties.

Scientists have found numerous ligands of a membrane-bound protein implicated in an unusual array of pathologies from neurotoxicity to prostate cancer. The ligands will help unravel diverse functions and develop targeted therapies.
Understanding how influenza virus evolves within its host is central to predicting the emergence and spread of new strains.
Sudden cardiac death (SCD) due to cardiovascular disease is the number one killer globally. EU-funded researchers worked on understanding the mechanisms leading to SCDs.
A European study pursued a new avenue in the design of drugs against malaria: it explored gene translation in the parasite Plasmodium falciparum as the target.
A European research initiative is continuing development of the skin substitutes Novomaix, denovoDerm and denovoSkin. Clinical studies are testing a one-step surgical procedure.
Stem cells are capable of self-renewal and give rise to specialised cell types. EU research has delved into the biochemical cascades involving signalling proteins and stem cells in the early development of germ layers in the embryo.
A European project is uniting the study sets of the European Biobanking and Biomolecular Resources Research Infrastructure (BBMRI) and other large trials such as the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). The result will be a multidisciplinary, international research initiative on a uniquely massive scale that can deliver an unprecedented amount of data on diseases.

Improving health care in Africa requires policymaking that is based on research evidence that is often inaccessible or incomprehensible for policymakers. An EU-funded project aimed to make research more accessible to policymakers.

An EU project is developing experimental systems and models to replace animals in testing for toxicity effects of new cosmetic and pharmaceutical products.
Positron emission tomography (PET) is the most popular method for verifying that the dose delivered to patients undergoing proton therapy is correct. Now, EU-funded researchers have designed a dedicated PET system that promises to improve the precision of proton dose measurement.
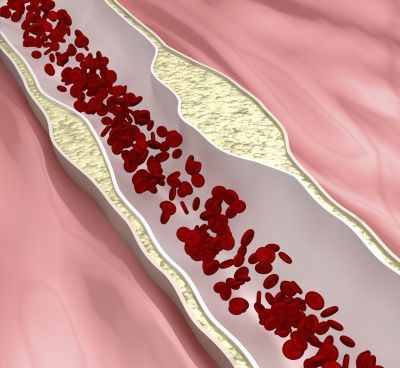
Atherosclerosis is a build-up of plaque on the inner walls of the blood vessels, and complications related to it are a major cause of mortality. Scientists are now conducting the first-ever clinical trials of nanosystems for its imaging, diagnosis and therapy.

Wound healing is a global challenge and different complementary treatment solutions have been developed worldwide. EU funding supported an initiative to bring together wound healing research groups through enhanced communication and knowledge transfer.
Patients with heart conditions are at high risk of suffering from secondary cardiovascular complications. Treatment generally entails a complex cocktail of medications leading to high costs, inappropriate prescription and poor patient compliance.
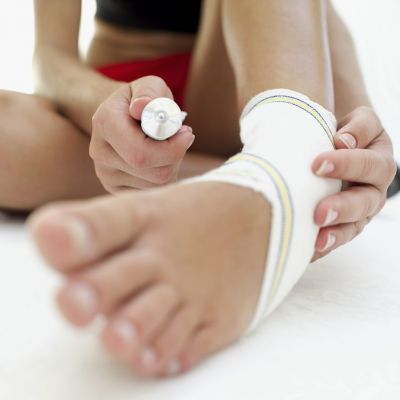
An innovative wound dressing promises to alert for infections and tackle bacteria by locally delivering antimicrobial agents on-demand. This is achieved by integrating natural biological processes with nanotechnology materials.
























