Fungal diseases result in millions of deaths annually, and the emergence of drug resistance to the limited repertoire of currently available antifungal medicines is aggravating this problem. EU funding is enabling researchers to find solutions.

EU-funded researchers worked on building a cheap and simple handheld device that can detect drug-resistant bacteria in a matter of hours rather than days.
EU funding supported an exciting venture that has developed smart magnetic solutions to safely and cost-effectively perform minimally invasive surgery. This could reduce health care costs and speed up patient recovery.

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammation of the gut. A European consortium is following a systems medicine approach for disease management.

Inkjet printing of a microdroplet containing a single living cell has become a reality. EU-funded partners who made it possible are now developing specific modifications to extend applications and commercialise outcomes.
Understanding how drugs can induce allergic responses is central to designing diagnostic tests and taking prompt action.
An international alliance has joined forces to integrate research efforts worldwide towards providing a cure for malaria.
A European consortium is working on delivering an immune-modulating agent at the tumour site. The results from the clinical trial for Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) treatment could also be used for treating other types of cancer.
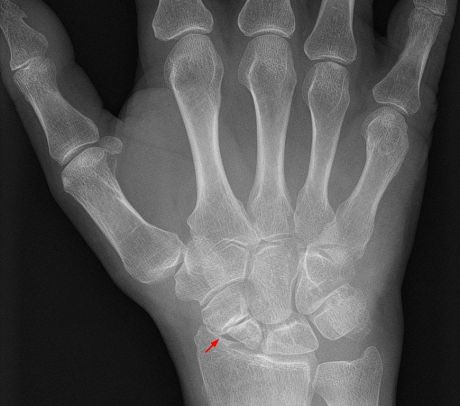
Millions die from road traffic injuries and several millions suffer from non-fatal injuries, with head and leg fractures being the most common injury sustained. Currently available bone implants are inadequate for healing such complex fractures.
A European consortium is putting a novel regenerative human heart valve to the test that may revolutionise the field of cardiovascular tissue engineering. Based on a special technology that removes all biological material from the valve, this novel medical product boosts immune tolerance and longevity.
European scientists are working on a new pharmacological intervention on energy metabolism as a new strategy for tackling diabetes.
European researchers investigated the mechanism implicated in sepsis-mediated organ damage. A new role for neutrophil-releasing structures was revealed with therapeutic implications.

The number of elderly people in the European population is steadily rising, placing greater demands on health care systems. Age-related conditions such as eye cataract and osteoarthritis need cost-effective treatment solutions.
In many cases, liver transplantation is threatened by hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. A European consortium hopes to improve liver graft survival through the administration of antibodies that block virus infection.

Improving the therapeutic response of cancer patients is a major medical challenge. A European study is working on novel drugs and innovative tools for predicting treatment outcome.
Current projections estimate that lung and pancreatic cancer will be the main causes of cancer-related deaths in the next decades. European researchers joined forces to facilitate substantial progress in their management.
European researchers worked to delineate the mechanism that links metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes with cancer.

Uncorrected refractive errors are the second leading cause of blindness. An EU-funded study is developing a biomechanical model to predict the outcome of laser-based refractive eye surgery, a procedure that can prevent blindness.

Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) control the passage of large molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Research revealing possible supramolecular mechanisms could be important in advancing targeted therapies for viral infections.
The maternal womb environment plays a crucial role in foetal development. By focusing on epigenetic and metabolic parameters, European scientists are working to understand their impact on embryonic development and improve overall human health.

Inflammation helps maintain health, but unresolved inflammatory responses can alter tissue homeostasis and cause disease. European researchers are targeting the physiological mechanisms that resolve inflammation to treat chronic inflammatory conditions.
Infections that occur in the hospital are a major health concern in Europe, as well as a significant economic burden. An EU initiative developed a novel process to create antimicrobial textiles for use in hospitals.
Relapsed high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC) is the main cause of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC)-related morbidity and mortality. EU-funded researchers are investigating factors contributing to recurrent EOC to find novel solutions.

Means to increase hypnotic suggestibility may provide individuals with more options in treatment of pain as well as psychological and neurological issues.
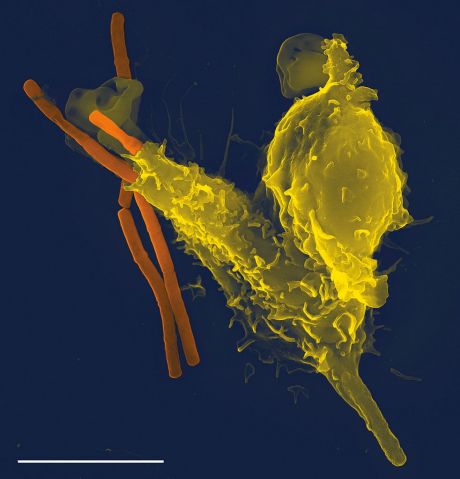
Aberrant immune responses are linked to cancer progression and transplantation rejection. EU-funded researchers worked on targeted immune modulation to improve patient outcomes.
























