Cancer remains the second most common cause of death in the EU despite recent significant advances. The development of more effective targeted therapies could dramatically improve the way we treat the disease.
Anti-cancer research never sleeps. Scientists are always in the process of discovering and developing new, more specific and less toxic drugs.
In-depth research and training in palliative care have yielded new tools and policy recommendations to raise the standard of living for ageing Europeans.
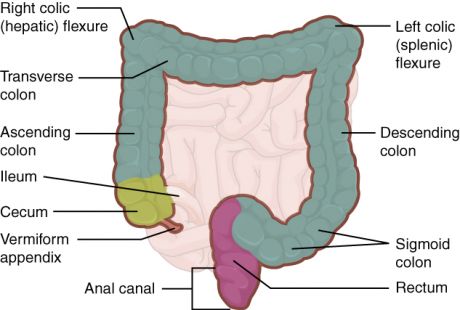
A major limitation of targeted therapies for colorectal cancer is the emergence of secondary resistance. European scientists are prospectively screening for genes that mediate such acquired resistance, aiming to identify specific drug resistance biomarkers.
European scientists have created the NaNose, a device that can detect lung cancer from the breath of a patient in less than 10 minutes.
Understanding the process of cardiac regeneration is of fundamental importance for the design of regenerative therapies. Many chronic cardiomyopathies and myocardial infarction lead to cardiac muscle death. If apoptotic cardiomyocytes do not get replaced this can lead to severe deficiencies in cardiac pump function.

Does work or the lack thereof affect health? An EU initiative shed light on the consequences of work on health.

Researchers have created molecules whose shape and surface chemistry mimic that of double helical DNA

Researchers have studied data from the International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) and found that insertions of genes or parts of genes are commonplace in cancer genomes.
Scientists have developed a rapid new method to analyse blood for signs of cardiovascular disease.
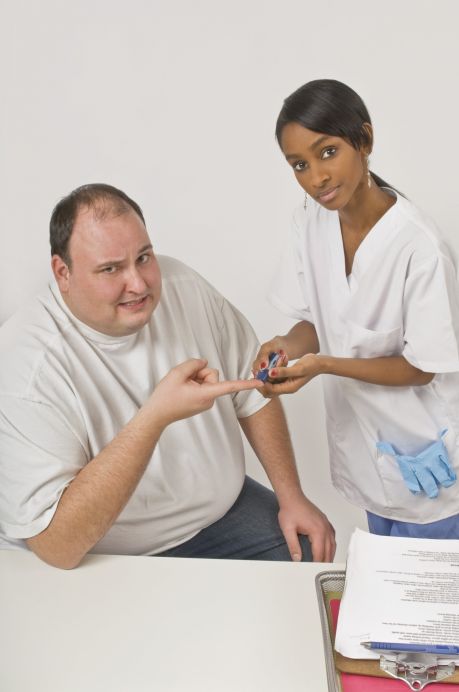

Patients with diabetes are living longer. Primary care is targeting the increased number of patients with associated kidney disease as well as cardiovascular disease (CVD).

Advances in modern medicine substantially increase life expectancy for the EU's ageing population, saving lives of patients with previously fatal diseases. As a consequence, there is an increased number of patients with chronic medical conditions.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease associated with increased levels of immunoglobulin D (IgD). Understanding the connection between the two will lead to improved therapies for SLE.
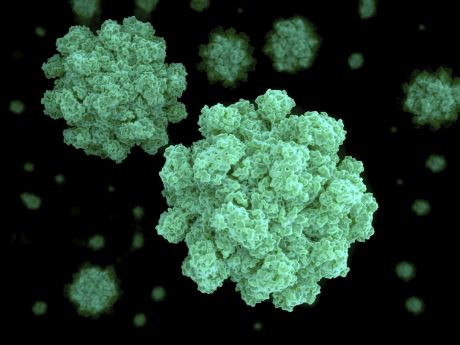
European researchers joined forces to unravel the function of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in breast cancer. The generated knowledge will drive the future of translational medicine.
According to the World Health Organisation, there are approximately 3 million people worldwide, who are obese or suffer from diabetes. Finding a cure necessitates going back to the drawing board and investigating cell biology.
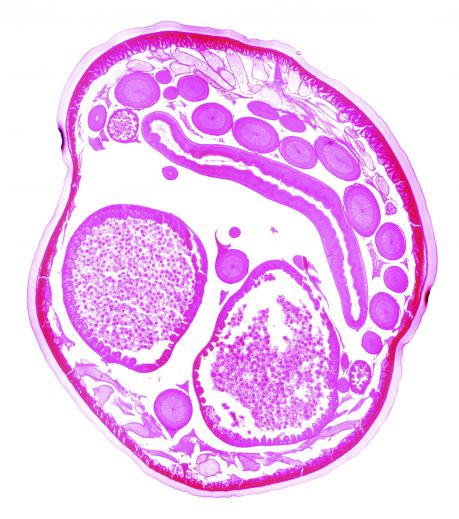
European researchers set out to dissect the process of protein aggregation, a hallmark of many degenerative disorders. Identification of the key players in amyloid formation may lead to novel therapeutic targets.

Characterising the interaction of bacteria with the human body should lead to a deeper understanding of human biology and disease and so help improve our overall well-being.
European researchers investigated the role of host proteins in Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. The findings may serve as the basis for innovative new therapies.
Through manipulation of epigenetic modifications, scientists hope to establish a new line of anti-cancer therapies. However, the emergence of therapy resistance necessitates investigation into the underlying mechanism.
Even normal ageing causes a decline of memory functioning is an indisputable fact. An EU-funded project has evaluated young and old to get information for feeding more reliable computational models of ageing and its effects.

An EU-funded project is investigating the benefits of palmitoleate (PAO) for the treatment of atherosclerosis and inflammation. Macadamia nuts and sea buckthorn are particularly rich in this omega-7 fatty acid – vegetarians can also benefit.

Somatic stem cells are present in most tissues and contribute to tissue homeostasis by replenishing short-lived cells. Understanding how this occurs is key for regenerative medicine.
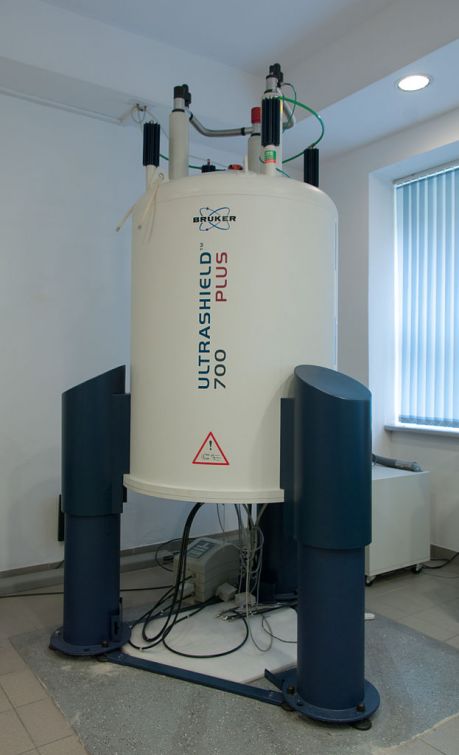

Determining the structure of biological components is key to understanding biochemical pathways in living tissue. EU funding supported the development of European nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) infrastructures for biological applications.
The annual healthcare expenditure in Europe arising from neonatal medical conditions with an acute threat to the brain is currently billions of euros. However, current practice and equipment in this field are far from optimal.
The inflammasome is a biochemical pathway and a key innate element in fighting infections. The downside is that its action is involved in some inflammatory syndromes.























