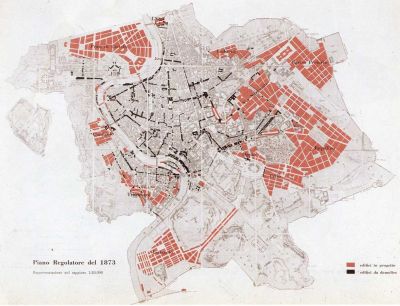
China and Europe are taking different routes to managing how their cities grow and change over time. An EU initiative explored the two approaches through academic and scientific exchanges.
In the 1960s, Intel's co-founder Gordon Moore predicted that the number of transistors on a chip would double about every two years. As that law seems to be hitting its barrier, scientists have demonstrated the utility of molecular electronics.
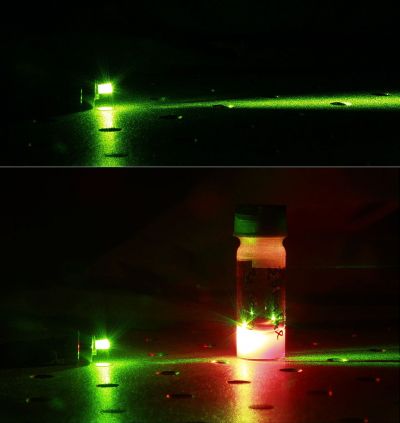
Lasers emitting green light currently have limited efficiencies, power and lifetimes. EU-funded scientists have made important progress towards novel technology that could change that in the near future.

The quantum world is a frontier of discovery and new applications. An EU-funded training network has provided a turboboost to an emerging field exploiting photons in novel quantum optoelectronic devices.
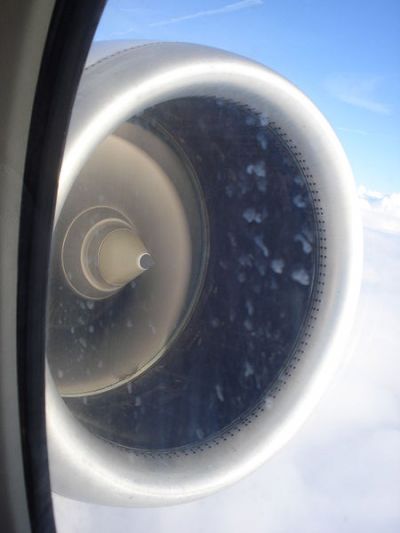

Production costs can be very high for large, rotating aeroengine structures requiring stringent structural integrity. Delivery of a component targeted for future aircraft will prove the feasibility of a new manufacturing technology.

Today's passenger and cargo ships are increasingly large and complex. Replacing conventional steel with other materials promises to minimise their susceptibility to cracking in areas where stress concentrates due to fatigue loads.

Novel coating materials and processing technology will soon make a rainbow of colours available for inexpensive consumer-oriented products such as home appliances and chandeliers.
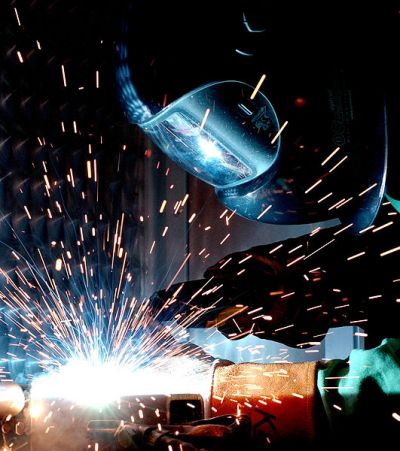

Nuclear power plants employ lots of metal structures often from dissimilar metals that must be welded together. Scientists are developing the basis for currently non-existent standardised tests of these welds to minimise overly conservative and costly inspection.

Production costs can be very high for large, rotating aeroengine structures requiring stringent structural integrity. Delivery of a component targeted for future aircraft will prove the feasibility of a new manufacturing technology.

Traditionally, how polymer parts perform under conditions of high heat is determined through extensive empirical work, which is time consuming and costly. EU-funded researchers, aided by the growth of numerical simulations, developed a more systematic approach to predicting their operational efficiency.

Holography provides a non-trivial connection between conventional quantum mechanical theories of fields and particles and quantum theories of gravity. It is still unclear which quantum field theories have gravitational duals and which do not.

An EU team is creating a method for manufacturing superior metal components using advanced alloys and 3D printing. Early tests of the concept and equipment show promise, and the project is developing new standards.

Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from heavy-duty vehicles (HDVs) rose by more than one third between 1990 and 2010. An EU initiative intends to help reduce carbon footprint by developing a novel fuel-saving technology for heavy trucks.

Underground pipes are one of the most efficient ways to move fluids long distances, but they are difficult to inspect. Robotic pigs carrying advanced ultrasound technology will soon be able to quickly and accurately assess pipes from within.
It has only been about 10 years since pioneering experiments started on quantum gases trapped by laser beams. Now, scientists have pointed the way to use of a highly sensitive technique for manipulation of the spin of a single atom in such a system.

The idea of a circular runway for airports could help revolutionise air travel, shortening flight times, saving fuel costs and promoting airport efficiency.
Particle accelerators have become critical tools, with more than 17 000 in operation around the world in research institutes, industry and hospitals. An EU-funded training network is preparing young researchers in the skills required to optimise them.

Maritime transport accounts for nearly 90 % of total world trade, and traffic at ports is expected to double over the next 2 decades. To meet this rocketing demand, an EU initiative introduced an innovative technology to enhance port efficiency and safety.

Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) exploiting expanded graphite (EG) fillers are a pioneering new material technology. Novel microwave (MW) heating will cut processing times and energy consumption to enhance market uptake.

Amid the demand for high-value perishable goods and the evolving appreciation of food safety, the refrigerated transportation market is booming. An EU initiative is addressing the costly energy consumption of the fleet's cold transport vehicles.

Polymeric composites have helped reduce aircraft weight without sacrificing performance. EU-funded scientists have advanced the state of the art and delivered design, processing and certification guidelines to the EU aerospace manufacturing sector.
Understanding the evolution of superexcited states (above the threshold for electron emission) could lead to control of chemical reactions. A novel experimental system to initiate and study such states will support related work.

An EU project is assessing the technical and market potential for self-healing in various materials, including polymers, polymer composites, concrete and ceramics. The novel processes show promise.

Friction between solids in contact arises in a wide range of engineering applications, limiting the lifetime of mechanical systems. As the physical mechanisms governing friction span different spatial and temporal scales, EU-funded scientists developed a multi-scale modelling framework.
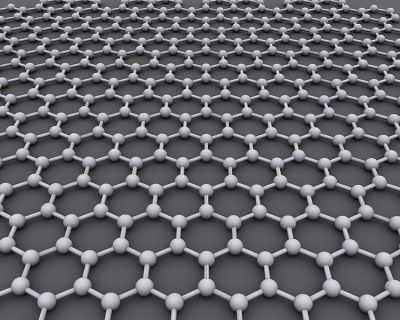
EU-funded scientists made important advances in understanding the properties of graphene-based nano-structured systems that open up practical use in optoelectronics.
























