
EU-funded scientists combined metallic nanostructures with semiconductor nanocrystals to significantly improve light trapping in solar cells and photodetector devices.

The traditional wood-making industry is transforming thanks to breakthrough engineering technology that produces high-quality lightweight wood panels at low cost.

A European project sought to improve the test definition to ensure interoperability of trains taking into account the ERTMS Level 1-2 communications and signalling systems.

Metal–air batteries could be a promising alternative to conventional lithium-ion (Li–ion) technology used today for electric cars. New electrode technology and cell designs are expected to overcome current barriers to rechargeable versions.

An innovative road surface containing an important amount of recycled car tyres and bound with an elastic resin could reduce traffic noise in an extreme way, i.e. comparable with a 3 m high noise screen, while providing an eco-friendly alternative for disposing of end-of-life tyres.

The time it takes manufacturing small and medium-size enterprises (SMEs) to generate products or services ahead of anticipated increases in demand has a direct impact on the future competitiveness of the sector in Europe. An EU initiative is developing innovative technologies to increase the efficiency of manufacturing.

EU-funded scientists are exploring nanocarbon electron sources to shed light on glowing materials for use in flat panel displays. Strong electron beams for electronic microscopes and vacuum electronic devices are other possible applications.
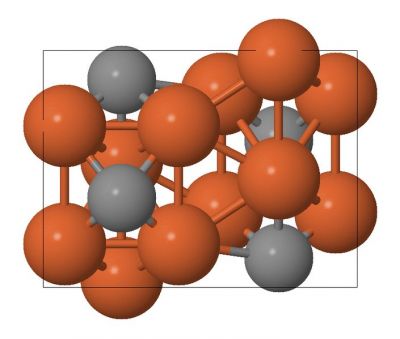
Metal-based catalysts for the production of carbon-containing compounds are an important pillar of organometallic chemistry. An evolution is underway to change from use of precious metals to more abundant and cost-effective catalysts and iron is a promising candidate.

An EU-funded project is working on developing three generations of lithium–sulphur (Li–S) battery prototypes. Overcoming the main obstacles that cut the Li–S battery life short should pave the way for promising applications in the automotive industry.
An EU-funded project is building a common theoretical framework with notions derived from physical, chemical and mathematical studies to describe the complex dynamics in laser–matter interaction.

Fibre-reinforced plastics (FRPs) are the building block of numerous aerospace structural components made with stacked configurations. EU-funded scientists have conducted extensive testing and numerical modelling to identify critical failure criteria.

EU-funded scientists have been developing a novel heating solution to efficiently repair composite parts in aircraft.

An EU-funded project is studying the temporal behaviour of electron dynamics in bulk materials. Using ultrafast pulses (attosecond) to probe electron energy bands represents initiation of a new field in condensed matter physics.
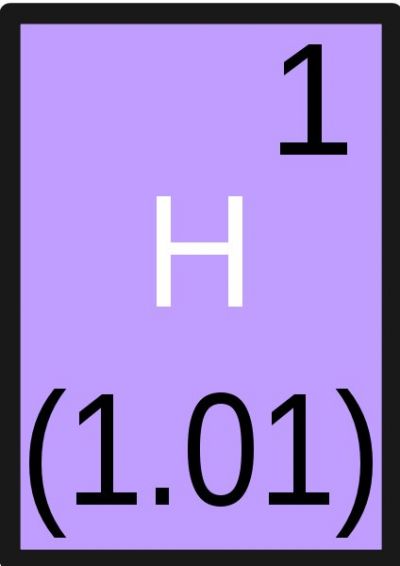
Reactions that transfer hydrogen or protons (hydrogen ions) are among the most elementary yet important reactions in industrial and biological systems. A new computational framework describes them efficiently and accurately for the first time.

More-electric aircraft (MEA) systems feature highly integrated electrical networks in avionics applications. EU-funded scientists are designing a passive cooling system to address thermal management of electrical hardware to guarantee its successful operation and enhance its performances.

Reducing the acoustic and pollutant emissions associated with air travel has important and broad-sweeping effects for citizens, industries and the environment. A novel acoustic liner for critical aeroengine components will make a major contribution.
An EU-funded project is blasting transition-metal molecules and others with extreme ultraviolet (XUV) radiation to probe their dynamics. The study has important implications for excited-state processes such as DNA photoprotection, light harvesting and atmospheric chemistry.

Noise is a serious drawback that lots of powerful technologies have. EU-funded scientists sought to improve methods of dampening the noise that aircraft engines generate.

An EU group has contributed to the aviation industry's ability to innovate and rapidly meet the demand for new aircraft. The team targeted 13 economic and environmental priorities, while also clarifying relevant funding and international collaboration opportunities.

The Piezo Institute is a hub of European expertise and resources in piezoelectric devices and materials including ceramics, single crystals, polymers and composites that have far-reaching applications in numerous sectors. An EU initiative is strengthening its visibility by increasing dissemination and further developing education, research and training activities.

Compressed air is often called industry's fourth utility after electricity, natural gas and water. Novel monitoring technology will now make sure the air supply is not contaminated with oil, a common and problematic condition.

A new EU-funded research project combined two cutting-edge technologies for major enhancements in cost-effective photodetector technology. Applications abound from digital photography to biomedical imaging.
Nonlinear optical effects are behind a number of very important phenomena and their experimental and industrial application. EU-funded scientists characterised promising new materials that could support enhanced instrumentation.
New research into systems chemistry is generating advanced materials with unique features like self-assembly and self-replication. These may find use in anti-counterfeiting measures and various other biological and electronic applications.

Geometric mechanics exploits the fact that both geometry and symmetry principles underly most physical laws. An EU-funded research network pursued modern applications sharing the same concepts of symmetry and geometry.
























