
Road slipperiness contributes to car accidents and fatalities. An EU initiative set out to design novel tools and techniques to measure and ultimately prevent the loss of skid resistance.

EU-funded researchers have developed a robot capable of sorting through and folding piles of rumpled clothes.

Ensuring a secure supply of energy with a focus on renewable energy sources is one of the major challenges of the 21st century. Smart anti-corrosion and anti-fouling coatings that withstand harsh marine environments will help achieve these goals.
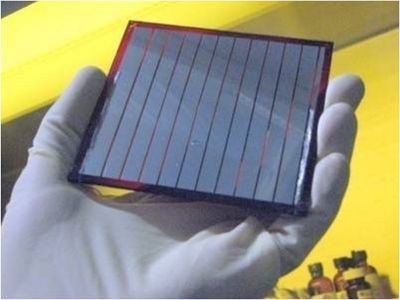
EU-funded scientists paved the way to more efficient and cost-effective organic photovoltaics (OPVs) through new material design and novel spectroscopic techniques.
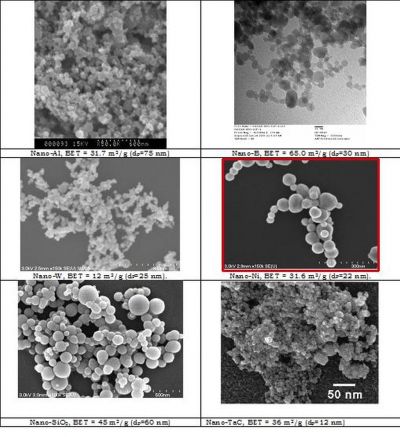
Quantum dots (QDs) are nanocrystals of semiconductor materials so tiny that they are considered dimensionless. Scientists explored their growth and integration in novel lasers as an alternative to conventional solid-state devices.
A European research project has made an important step towards the further miniaturisation of nanoelectronics, using a highly-promising new material called silicene. Its goal: to make devices of the future vastly more powerful and energy efficient.
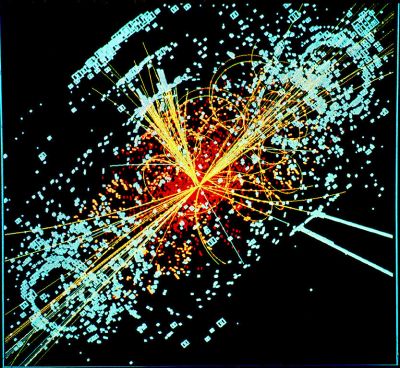
Discovery of the Higgs boson confirmed the last remaining piece of the standard model, the theory enabling our current understanding of matter and energy at the most fundamental level. EU-funded scientists searched for deviations from this theory, which might offer a deeper understanding of physics.

Cavity optomechanics is an area of research exploring the interactions between light and matter at the boundary between the classical and quantum mechanical regimes. Novel setups and experimental protocols have made exciting new experiments possible.

Magnonics is an emerging and rapidly growing field of research dealing with magnetic phenomena associated with spin waves, a magnetic analogue of sound or light waves. EU-funded scientists have pushed the frontiers of understanding in this field towards creation of a novel type of metamaterials – so called magnonic metamaterials.
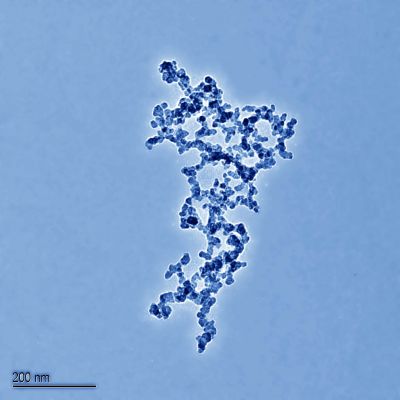
Information concerning the potential hazardous effects of manufactured nanoparticles on human health is urgently required. The fellow of the Intra-European Fellowships (IEF) examined how nutrition can protect against nanoparticle toxicity.

Interchanges where passengers can switch from one public transport route to another more safely, reliably and comfortably benefit the mobility needs of European society overall. An EU initiative is looking to make urban transport interchanges more efficient and sustainable.

Researchers have developed protocols and information to standardise the manufacture of smart textiles.

Diamonds do not have to be large to be valuable, at least to scientists. Nanocrystalline diamond (NCD), superior to silicon for use in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), was exploited in novel MEMS devices, attracting large industrial investment.
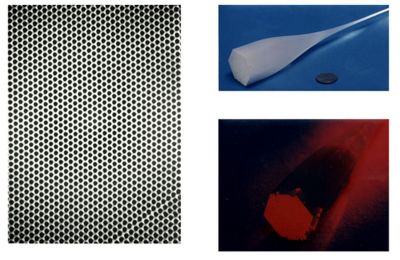
Engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) are now ubiquitous, but safety studies have lagged behind technological developments. EU-funded research will establish an ENM safety classifier akin to material safety data sheets to ensure safety for humans and the environment.

EU-funded scientists are using plasmonic nanocrystals (NCs) to shift the light-harvesting spectrum of solar cells to the near-infrared region.

EU-funded scientists combined metallic nanostructures with semiconductor nanocrystals to significantly improve light trapping in solar cells and photodetector devices.

The traditional wood-making industry is transforming thanks to breakthrough engineering technology that produces high-quality lightweight wood panels at low cost.

A European project sought to improve the test definition to ensure interoperability of trains taking into account the ERTMS Level 1-2 communications and signalling systems.

Metal–air batteries could be a promising alternative to conventional lithium-ion (Li–ion) technology used today for electric cars. New electrode technology and cell designs are expected to overcome current barriers to rechargeable versions.

An innovative road surface containing an important amount of recycled car tyres and bound with an elastic resin could reduce traffic noise in an extreme way, i.e. comparable with a 3 m high noise screen, while providing an eco-friendly alternative for disposing of end-of-life tyres.

The time it takes manufacturing small and medium-size enterprises (SMEs) to generate products or services ahead of anticipated increases in demand has a direct impact on the future competitiveness of the sector in Europe. An EU initiative is developing innovative technologies to increase the efficiency of manufacturing.

EU-funded scientists are exploring nanocarbon electron sources to shed light on glowing materials for use in flat panel displays. Strong electron beams for electronic microscopes and vacuum electronic devices are other possible applications.
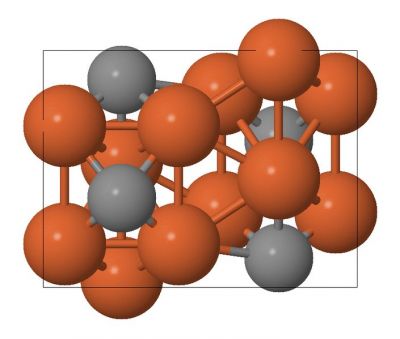
Metal-based catalysts for the production of carbon-containing compounds are an important pillar of organometallic chemistry. An evolution is underway to change from use of precious metals to more abundant and cost-effective catalysts and iron is a promising candidate.

An EU-funded project is working on developing three generations of lithium–sulphur (Li–S) battery prototypes. Overcoming the main obstacles that cut the Li–S battery life short should pave the way for promising applications in the automotive industry.
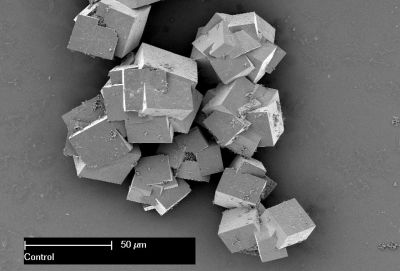
An EU-funded project is building a common theoretical framework with notions derived from physical, chemical and mathematical studies to describe the complex dynamics in laser–matter interaction.























