
Anti-reflective glass is a component of products used in devices ranging from mobile phones to solar cells. Extensive materials and process development by EU-funded scientists should help meet the increasing demand for harder coatings that withstand harsh environments.

Non-destructive testing (NDT) methodologies to evaluate the sub-surface status of steam pipes operating at very high pressures and temperatures is lacking. Novel ultrasound technology could soon decrease the incidence of dangerous failures.

A multidisciplinary, international look at knowledge exchange sheds light on how regionalisation and globalisation redefine the nature, mission and scope of universities.

An EU research team is working on ways to stream video over standard wireless networks. This will be achieved through improved algorithms, coding and networking, leading to a mature software product.

An EU project is helping European cities adopt and implement previous innovations in transportation technologies. Addressing 15 concepts and 10 cities to start with, the work will yield practical handbooks and training programmes.

A novel technology platform exploiting a wide range of X-ray methods (including robot based setups) will facilitate the acquisition of high precision X-ray and X-ray computed tomography (XCT) images of composites. The aerospace industry is thus entering a new era in non-destructive testing of aeronautic components.

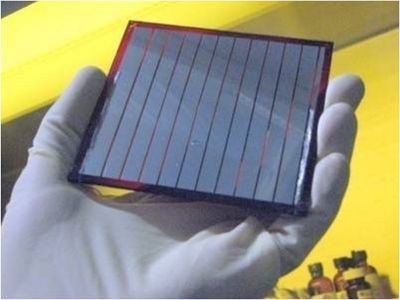
An EU-funded project sought to enhance the efficiency of crystalline silicon (Si) solar cells by growing nanometre-scale localised structures.
A crucial part of artificial photosynthesis is water oxidation — separating the hydrogen from the oxygen. EU-funded scientists designed metal-based catalysts to efficiently mimic natural processes for a greener future.

The era of mass production of similar items is coming to an end with a need for rapid production of smaller batches of niche products. A novel industrial control platform promises to help EU manufacturers evolve to meet customer demands.

Passenger comfort is an increasingly important part of the design of aeroplane interiors, and temperature and lighting are critical aspects, particularly on long flights. Novel smart aeroplane windows that adjust lighting and heat will make air travel cosier.

Road slipperiness contributes to car accidents and fatalities. An EU initiative set out to design novel tools and techniques to measure and ultimately prevent the loss of skid resistance.

EU-funded researchers have developed a robot capable of sorting through and folding piles of rumpled clothes.

Ensuring a secure supply of energy with a focus on renewable energy sources is one of the major challenges of the 21st century. Smart anti-corrosion and anti-fouling coatings that withstand harsh marine environments will help achieve these goals.
EU-funded scientists paved the way to more efficient and cost-effective organic photovoltaics (OPVs) through new material design and novel spectroscopic techniques.
Quantum dots (QDs) are nanocrystals of semiconductor materials so tiny that they are considered dimensionless. Scientists explored their growth and integration in novel lasers as an alternative to conventional solid-state devices.
A European research project has made an important step towards the further miniaturisation of nanoelectronics, using a highly-promising new material called silicene. Its goal: to make devices of the future vastly more powerful and energy efficient.
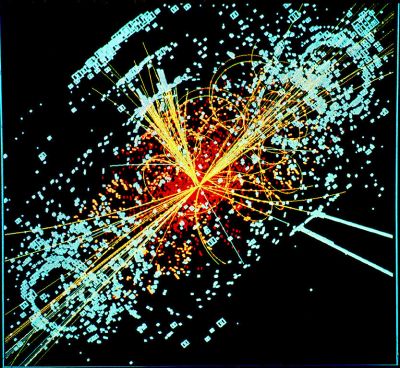
Discovery of the Higgs boson confirmed the last remaining piece of the standard model, the theory enabling our current understanding of matter and energy at the most fundamental level. EU-funded scientists searched for deviations from this theory, which might offer a deeper understanding of physics.

Cavity optomechanics is an area of research exploring the interactions between light and matter at the boundary between the classical and quantum mechanical regimes. Novel setups and experimental protocols have made exciting new experiments possible.

Magnonics is an emerging and rapidly growing field of research dealing with magnetic phenomena associated with spin waves, a magnetic analogue of sound or light waves. EU-funded scientists have pushed the frontiers of understanding in this field towards creation of a novel type of metamaterials – so called magnonic metamaterials.
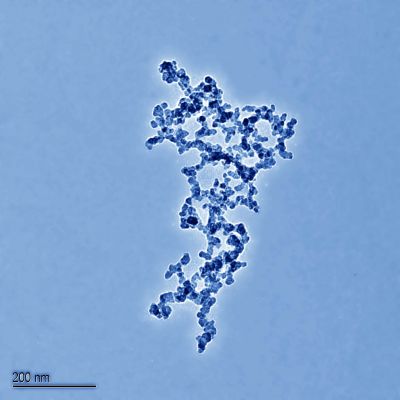
Information concerning the potential hazardous effects of manufactured nanoparticles on human health is urgently required. The fellow of the Intra-European Fellowships (IEF) examined how nutrition can protect against nanoparticle toxicity.

Interchanges where passengers can switch from one public transport route to another more safely, reliably and comfortably benefit the mobility needs of European society overall. An EU initiative is looking to make urban transport interchanges more efficient and sustainable.

Researchers have developed protocols and information to standardise the manufacture of smart textiles.

Diamonds do not have to be large to be valuable, at least to scientists. Nanocrystalline diamond (NCD), superior to silicon for use in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), was exploited in novel MEMS devices, attracting large industrial investment.
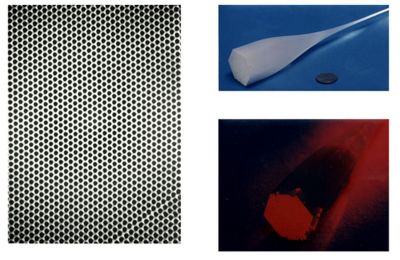
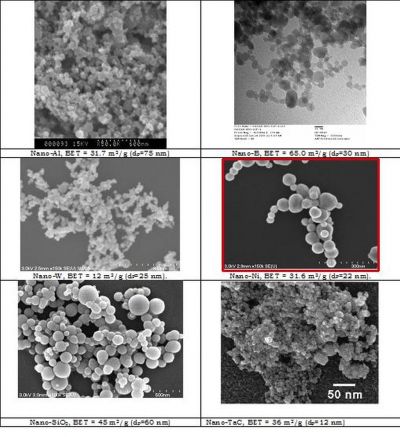
Engineered nanomaterials (ENMs) are now ubiquitous, but safety studies have lagged behind technological developments. EU-funded research will establish an ENM safety classifier akin to material safety data sheets to ensure safety for humans and the environment.

EU-funded scientists are using plasmonic nanocrystals (NCs) to shift the light-harvesting spectrum of solar cells to the near-infrared region.






















