
EU-funded scientists are modelling and testing key composite structures in alternatively powered vehicles (APVs). Investigating the crashworthiness of these lightweight materials is crucial to increasing their widespread commercial uptake.

Engineers have been experimenting with tiny structures called riblets that reduce drag over aircraft wings. An innovative robotic platform for application should speed things along, making sure important benefits are felt in the near future.

Although most people think of the jet engines when aircraft noise is mentioned, airframes contribute significantly to noise radiated by modern aeroplanes. An innovative and efficient modelling suite is pointing the way to new low-noise designs.

An EU-funded initiative has set out to reinforce Europe's leading role in laser science by consolidating and extending an interdisciplinary network of national top-flight laser facilities.

An EU-funded project developed reliable snowmaking equipment that is more efficient, silent and economical compared to the state of the art.

Cement continues to be an important global construction material. EU-funded scientists developed models and experimental methods to facilitate utilisation of waste streams as supplementary cementing materials (SCMs) for greater sustainability.
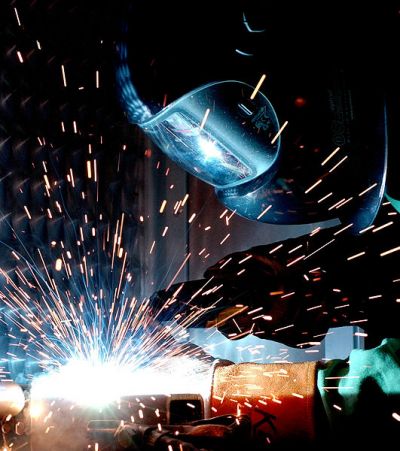

EU-funded researchers are developing a cost-effective, low-distortion welding process applicable to steel to help European shipyards maintain competitiveness.

An EU-funded project investigated methods for controlling battery power flow in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) to minimise ripple currents. Project results should allow obtaining high-performance, cheaper and more compact batteries and capacitors.

Un proyecto financiado con fondos europeos investigó métodos para controlar el flujo de carga de la batería en vehículos eléctricos híbridos (VEH) a fin de minimizar las corrientes de rizado. Los resultados del proyecto deberían facilitar la obtención de baterías y capacitadores más económicos, compactos y de alto rendimiento.

Only a fraction of the energy released by burning fossil fuels is converted into mechanical or electricity energy with most of the energy released as heat and written off as a loss. Thermoelectric materials developed by an EU-funded project may provide the solution to this energy problem.

An EU team developed robots that automatically inspect welds in ship hulls. The various fault-detection methods, plus robotics and control systems, were successfully tested on hull plating at the Chalkis shipyards in Greece.

Despite the growing popularity of automated transport systems, take-up is lagging because of the operational and legal frameworks currently in place. An EU initiative plans to remove barriers with the rollout of driverless vehicles.

European researchers have developed an algal management system based on ultrasound technology to control algal blooms that threaten public health and water quality.

Electrolysis is an important new technology for producing hydrogen as an energy carrier. An EU-funded project is developing novel materials for high-efficiency and cost-effective electrolysers.

An EU study studied the performance properties, including service life, of wood as a construction material. A re-analysis of historical data, with new testing, introduces new standards, enabling greater usage of this sustainable resource.
Moulded Interconnect Devices (MIDs) combine all the features of moulded plastic parts with electrical circuitry and electronic components assembled directly on the plastic package.

The widespread use of electric vehicles (EVs) could make a tremendous contribution to the reduction of urban pollution and global carbon dioxide emissions. Novel wireless charging technology with increased convenience and providing longer driving distances may tip the scales.

The market for multifunctional microsystems made of 3D layered materials is growing. A novel design and manufacturing platform promises to revolutionise the way things are done and enhance EU market position.
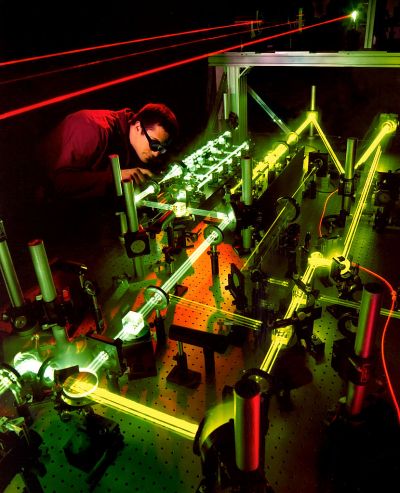
The use of ultrafast (femtosecond) laser sources to optically excite electrons in metals provides the basis for novel applications in the field of optoelectronics, including ultrafast switches. Young scientists advanced the field with EU support.

Accretion of ice on aircraft wings increases weight, reducing lift and affecting manoeuvrability. Novel electromechanical de-icing technology breaks off the ice through deformations and promises integration with newer more-electric aircraft systems.
An EU-funded project improved theoretical predictions regarding cross-sections of hadron scattering at high energies.

The use of ultrafast (femtosecond) laser sources to optically excite electrons in metals provides the basis for novel applications in the field of optoelectronics, including ultrafast switches. Young scientists advanced the field with EU support.

Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) in cars could reduce costs, weight and fuel consumption while enhancing performance. Researchers used advanced experimental and simulation tools to address their technically challenging implementation.

An EU-funded project is working on reducing the truck carbon footprint by developing a new type of truck tyre along with sensors and advanced trailer telematics.

Security of urban transport in European cities can be enhanced while also boosting the mass transport security industry.
























