
As the world is becoming more digital and connected, the transition from analogue to digital technologies can have a profound impact on materials and manufacturing. An EU-funded project has identified the most promising digital fabrication technologies and pointed out the direction to transform European industries.
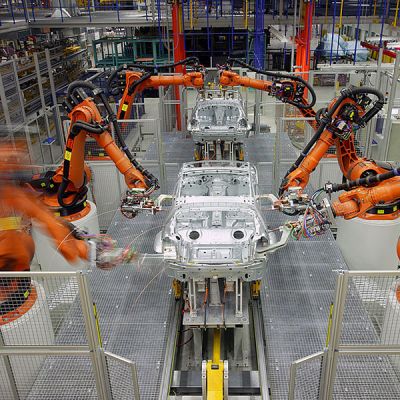
Adhesive bonding can increase the range of lightweight materials used by car manufacturers, but the high-temperature curing required is problematic. A novel formulation compatible with low temperature curing will have major impact.

European buildings account for approximately 40 % of Europe's total energy consumption and about 36 % of its carbon dioxide emissions. Zero net energy buildings are targeted and novel smart window technology could be the means to the end.

Reducing the environmental impact of road transport would have major benefits for the planet. Materials and processes that lead to a superior electric vehicle with minimal carbon footprint at a reasonable price should encourage widespread adoption.

Major energy savings and reductions in harmful emissions are a step closer with the development of viable superconducting tapes.
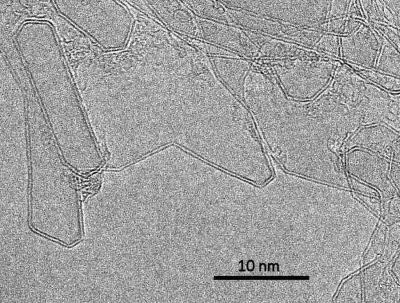
With the development of clean energy sources as one of the greatest challenges of the 21st century, the use of sunlight to drive catalytic reactions, and particularly hydrogen production from water splitting, has emerged as a promising route. This project takes advantage of the large library of nanomaterials to produce new hybrids with enhanced properties that result in higher photocatalytic efficiency.
An EU team created a web portal to promote the use and transfer of eco-innovation information. Project results included an analysis methodology, the evaluation of over 190 cases and a breakdown of the sectors showing the most promise.

Tapping the market for small, customised metal parts could boost the competitive position of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). A new manufacturing platform designed with this in mind promises better parts at lower prices.

Nowadays, critical parts of aero engines are manufactured at different factories in different countries, requiring that their inspection is done in a unified way. For EU-funded researchers, the best way to ensure homogeneity is by automating the evaluation of these parts.
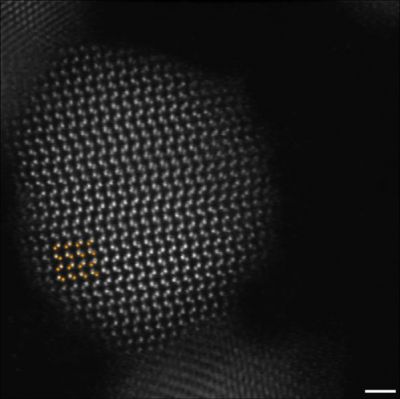
Nanoparticles (NPs) with dimensions on the scale of nanometres have improved products and services in numerous fields. However, their small size, high reactivity and tremendous diversity pose challenges to ensuring environmental health and safety.

DNA is an amazing natural polymer that self-assembles into complex 3D shapes. Scientists have demonstrated the ability to control configuration and make them conductive.

Plastics form the backbone of components in numerous industries including automotive, lighting and toy manufacturing. New moulds and mould tools that imprint nano-structured patterns directly during plastic processing will enable major improvements in production.

Proteins are ubiquitous, serving a myriad of important functions in living organisms from neurotransmission to cell recognition. Scientists have now engineered stable and functional protein modules for integration into novel nanodevices.

The design of a ship can adversely affect human performance, which may lead to maritime accidents. An EU initiative is looking at how ship design contributes to human error.

Europe's electric mainline railway systems provide an important service to individuals and businesses. Energy management solutions can enhance their sustainability, and a large EU-funded consortium plans to deliver a roadmap for implementation.

EU-funded scientists are modelling and testing key composite structures in alternatively powered vehicles (APVs). Investigating the crashworthiness of these lightweight materials is crucial to increasing their widespread commercial uptake.

Engineers have been experimenting with tiny structures called riblets that reduce drag over aircraft wings. An innovative robotic platform for application should speed things along, making sure important benefits are felt in the near future.

Although most people think of the jet engines when aircraft noise is mentioned, airframes contribute significantly to noise radiated by modern aeroplanes. An innovative and efficient modelling suite is pointing the way to new low-noise designs.

An EU-funded initiative has set out to reinforce Europe's leading role in laser science by consolidating and extending an interdisciplinary network of national top-flight laser facilities.

An EU-funded project developed reliable snowmaking equipment that is more efficient, silent and economical compared to the state of the art.

Cement continues to be an important global construction material. EU-funded scientists developed models and experimental methods to facilitate utilisation of waste streams as supplementary cementing materials (SCMs) for greater sustainability.
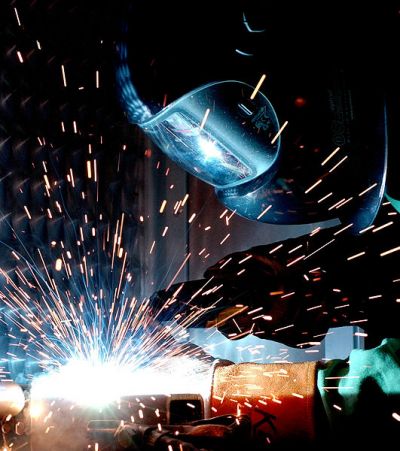

EU-funded researchers are developing a cost-effective, low-distortion welding process applicable to steel to help European shipyards maintain competitiveness.

An EU-funded project investigated methods for controlling battery power flow in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) to minimise ripple currents. Project results should allow obtaining high-performance, cheaper and more compact batteries and capacitors.

Un proyecto financiado con fondos europeos investigó métodos para controlar el flujo de carga de la batería en vehículos eléctricos híbridos (VEH) a fin de minimizar las corrientes de rizado. Los resultados del proyecto deberían facilitar la obtención de baterías y capacitadores más económicos, compactos y de alto rendimiento.

Only a fraction of the energy released by burning fossil fuels is converted into mechanical or electricity energy with most of the energy released as heat and written off as a loss. Thermoelectric materials developed by an EU-funded project may provide the solution to this energy problem.
























