
Optimal configuration of preliminary designs lays the foundation for final aircraft concepts that are ready to take flight. A new preliminary design platform integrates eight different analyses to optimise performance and cost effectiveness early.

Researchers are developing a varnish with antimicrobial, moisture and oxygen as improved physic-mechanical properties, to be used in food packaging industry.

Flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) with high operating temperatures could replace bulky cabling in high-temperature zones of aircraft engines. The weight and space savings should help achieve reductions in fuel consumption and emissions.

Greenhouse gas (GHG) inventories involve uncertainties because some data are unavailable, imprecise or incomplete and because of limited knowledge of some processes. Reducing this uncertainty is vital for maintaining the credibility, quality of compliance and proper functioning of carbon trading systems.

Robotic welding accounts for about one fourth of all industrial robotic tasks, yet automation is lacking. A novel low-cost robot with automatic track calculation and quality control will have major impact on quality, costs and competitiveness.

Should governments plan locally or regionally to reduce vehicle use? The answer is both, though with priority to the regional level, according to an EU study comparing urban form effects on vehicle travel at different spatial scales and contexts.

Lightweight aluminium (Al) alloys are an important pillar of aircraft development. With predicted future service conditions requiring higher operating temperatures, scientists explored new wrought alloys and thermal treatments to improve properties.

The assembly of automotive, aerospace, pharmaceutical and medical industries is intertwined with high labour costs in Europe. An EU-funded project is developing smart technology to reduce costs and enhance the effectiveness of complex assembly systems.

Unit load devices (ULDs) are special containers for aviation cargo, and generally arrive at the aircraft pre-loaded. While very successful and ubiquitous, they also represent the weakest link in aviation security.

Global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) are entering a new era of service with major updates to existing infrastructure and new additions to the family. A novel software-defined receiver may soon replace conventional hardware to take full advantage of the extended possibilities.

Hitherto maintenance of wind turbine blades (WTBs) usually involved an inspector descending a rope for a visual examination. EU-funded scientists have unveiled a novel automated system for in situ inspection that avoids perilous work at heights.

More than half of EU expenditures in the construction sector are on repair of existing structures, most commonly those made of reinforced concrete. An accelerated concrete curing system with significantly reduced energy consumption promises major benefits.

Increasing the density of stored information to enable ever-smaller devices with greater memory capacities has become the Holy Grail for magnetic memories. Multi-scale models are shedding light on the ultrafast mechanisms that will be required.
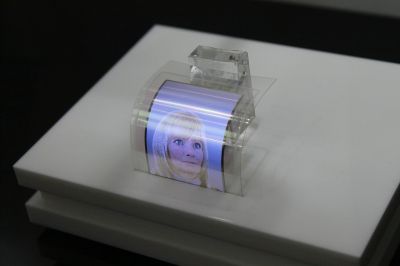
Novel lighting sources are required to reduce worldwide energy consumption. A European consortium worked to develop the necessary modelling tools for optimising an environmentally friendly lighting technology.

Polymer composites have increasingly replaced metal structures in the aerospace industry. Scientists have demonstrated the feasibility of integrating strain sensors for continuous monitoring of structural integrity and major improvements in safety.

Hybrid aircraft combining the best of an airship, plane, helicopter and hovercraft could provide major benefits in numerous applications. Scientists improved current concepts in a rigorous experimental and modelling campaign.

Data-tracking software initially designed to help support physicists at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) needed new capabilities. An EU initiative has set out to bring the software up to modern standards.

EU-funded scientists are developing a new generation of permanent magnets, shifting away from rare earth elements. These should be particularly attractive for electric vehicles and machinery.
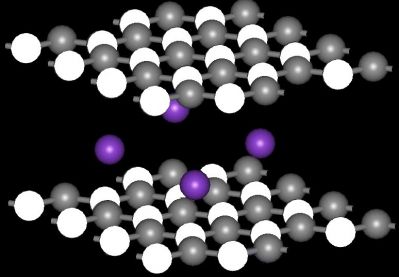
EU-funded scientists made important advances in understanding the thermomechanical and electronic properties of graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN).
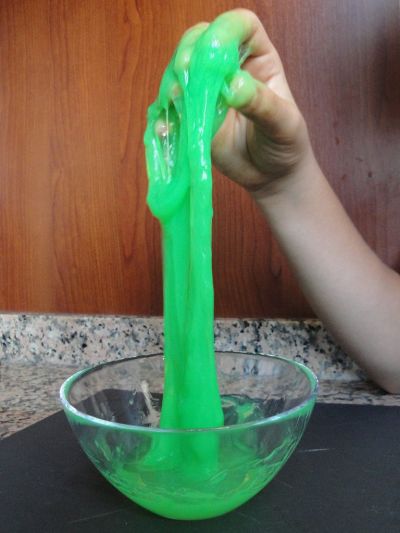

EU-funded scientists are developing a new era of plastic materials that have the ability to self-heal spontaneously, just like living organisms do. Such materials will have important implications for more durable vehicles and safer and more durable roads.

Thermal management is a hot topic in microelectronic and optoelectronic devices. An EU-funded project is working on integrating an innovative cooling system that unlike conventional solutions that use single-phase liquids or gases involves two-phase flows.
A mixed-design approach adopted by EU-funded companies and researchers allowed a first step in the creation of reliable European high-performance digital signal processor (DSP) able to meet the requirements of future space missions.

A transportation system based on personal aerial vehicles (PAVs) may slowly but surely be moving from the realm of science fiction to reality. Recent technological developments are laying the basis for this once far-fetched scenario.

Trains and ships are seen as effective alternatives for reducing high traffic and carbon emissions caused by road freight transport vehicles. An EU initiative is helping to ease the changeover to more energy-efficient transport means.

Although many studies address the potential toxicity of nanoparticles (NPs) to humans, important questions remain about the fate of NPs in soil. New research sheds light on factors affecting bioavailability and toxicity to soil-dwelling organisms.
























