Nanotechnology relies on nanomaterials with size scales on the order of atoms and molecules, which makes them particularly stealthy when it comes to entering the body. Teamwork is leading to a much-needed standardised system for risk assessment.
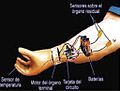
Prosthetic technology has advanced significantly, but complex movement has not yet been realised. EU-funded researchers worked on advancing signal processing, machine learning and pattern recognition to change the status quo for myoelectric systems.

EU-funded researchers have advanced a new generation of sustainable, smart printed products. Integrating paper and electronics they have developed highly functional, printable labels that can reveal temperature, toxicity or pollution levels.

Extracting, processing and manufacturing conventional building materials consume a tremendous amount of energy. Novel biocomposites are reducing that embodied energy and delivering high-performance, eco-friendly materials at no additional cost.

One of the open challenges in science today is to directly observe atomic motions as they occur. Ultrafast electron diffraction (UED) uses electron beams to achieve this goal.

Buildings account for approximately 40 % of total EU energy consumption. An EU project has developed new insulation solutions applicable to façades, wall cavities and interiors to transform buildings constructed before 1975 into energy efficient units, with minimal disruption for occupants.

Europe’s small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the composites business are battling competition from lower labour cost countries. High-performance composites made with low-cost injection moulding should shift the balance in favour of EU SMEs.

The average car uses approximately 40 to 50 square metres of fabric, and not only in its upholstery. Textile fibres are used in seat belts, interior panels, sandwich panels and more, so switching to biopolymers from polyester will make cars much greener.

Strong and lightweight metal and metal alloy components are cornerstones of products in the automotive, wind power and construction sectors. Novel nano-reinforcements and improved casting technologies will enhance product performance and industry sustainability.

Plastics and composites have improved products and applications in numerous industries, from automotive to biomedical to consumer electronics. Smart composite mould technology will advance the state of the art and expand markets for manufacturers.

Cities are challenged to come up with a form of transport mobility that is sustainable, energy efficient and respectful of the environment. An EU initiative is bringing together public stakeholders from European cities and the innovation community to realise sustainable zero-carbon transport systems.
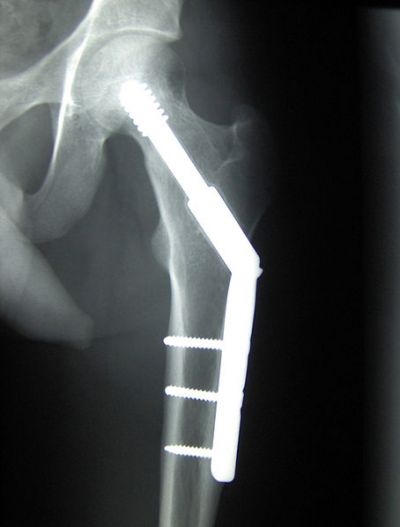
Ageing, trauma and poor lifestyle can all contribute to weak joints that sooner or later require implants for bone support or replacement. Current orthopaedic implants require revisions with time-consuming surgeries and long patient recovery time.

Two main drivers of global innovation and economic growth are the semiconductor/integrated chip (IC) market and renewable energy. Deeper understanding of the mechanisms of charge transport in advanced materials could advance both fields substantially.

As electronics miniaturisation approaches its technological limits, stacking is seen as a promising way to overcome the barrier. Scientists are developing the lacking yet vital technology to interconnect the layers.

The cost of replacing aeroplanes is driving the aviation sector to seek more cost-effective repair and maintenance solutions that will prolong the air-worthiness of existing fleets.

A very powerful platform that exploits mass spectrometry (MS) to simultaneously identify biologically relevant proteins, lipids and carbohydrates could change the face of clinical medicine.

Researchers are using low-value plant raw materials to produce bio-based synthetic fibres for the textile industry in a cost-competitive, energy-saving, and environmentally sustainable process.

Exploiting very hard materials in machine tools enhances durability, decreasing maintenance and repair costs and ensuring robustly reliable products of high quality. A novel laser-processing platform will support EU leadership in diamond-based tools.

The EU aims to play a leading role in the deployment of alternative propulsion technologies for sustainable mobility systems. An EU-funded initiative introduced innovative approaches for manufacturing energy-efficient and safe light urban electric vehicles (EVs).

EU-funded scientists identified new materials that could render lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries in electric vehicles (EVs) significantly more efficient and powerful.

Extracting, processing and manufacturing conventional building materials consume a tremendous amount of energy. Novel biocomposites are reducing that embodied energy and delivering high-performance, eco-friendly materials at no additional cost.

Hydrocarbons from crude oil are used to produce higher-value chemicals, but increasing price volatility has affected the competitiveness of EU manufacturers. Novel membrane reactors will use alternative feedstock to reduce dependence on oil.

Purity is paramount for any medicinal product. EU research is developing a DNA test for production of plant-based preparations.

An EU initiative helped launch a new European Centre of Excellence (CoE) for developing all-electric ships (AESs). The newly established CoE in Greece is set to play a critical role in the launch of the first generation of AESs.

Little tabs off the trailing edge of helicopter rotor blades that can be positioned according to flight conditions promise better lift and lower fuel consumption. EU-funded scientists are developing demonstrators of the related structural and control technologies.
























