
A recent project has promoted the uptake of information and communications technology and robotics solutions for the challenges faced by European agriculture.

EU-funded scientists developed an innovative laser optical procedure that allows measurement of material deformation in wind turbine blades.

Transportation is one of the key factors in European economic performance and competitiveness. An EU initiative is providing advice on how to most effectively invest in public and private infrastructure.

Optimising fuel cell technology can reduce noise and emissions. An EU initiative plans to unveil a portable power solution for powering devices in recreational vehicles (RVs).

There are roadblocks to designing and manufacturing lenses and frames based on specific end-user specifications and then making them commercially viable. An EU initiative has developed technology and flexible and easily reconfigurable business models to produce and bring to the market these new products.

Buildings in Europe currently account for approximately 40 % of its annual energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions. Low-cost, eco-friendly insulation technology will help Europe's small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) retrofit buildings effectively.

The amount of lightweight aluminium in new cars is increasing, but current methods to get rid of hydrogen gas (H2) bubbles that create porosities are expensive, inefficient and hazardous. Novel ultrasonic technology is headed to market to keep aluminium on the road.
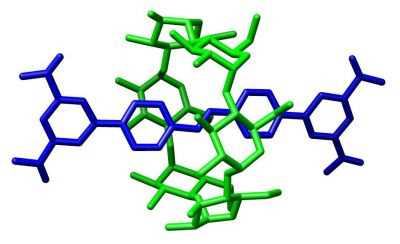
EU-funded researchers have married inorganic and organic building blocks for the assembly of rotaxanes that could one day be used to develop quantum computers.

Routine inspection and maintenance can be anything but routine in large industrial settings. An EU initiative has developed autonomous robotic technology to protect capital investment and promote human safety.

European small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) working in the cast iron foundry business require modernisation to remain competitive. A large European consortium is implementing lean manufacturing principles and advanced control to fill this need.

An EU team is developing an idea for unmanned shipping. The proposal involves designs for various modular on-board systems for ship control, sensing and communication, plus onshore stations.

Lithium-ion (Li-ion) rechargeable batteries are the standard in today's electric vehicles, but they need a recharge after about 150 km. Li-air batteries could soon change that, and pioneering work has highlighted design considerations.

Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is a biodegradable polymer formed from renewable resources, namely fermentation processes in several kinds of bacteria. Scientists have now overcome the main obstacle to using PHB: poor mechanical properties.

There is a plethora of long-term foresight studies on a cleaner, greener and more user-friendly European transport industry. An EU initiative aims to summarise all this available information and to compare and evaluate the various visions and policies to reach their intended targets.

There is growing interest in the potential and power of immersive technology for scheduled and emergency maintenance in extreme environments such as nuclear installations. An EU initiative is exploring the use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) – the blending of virtual reality and real life – for personnel safety systems.
Nanotechnology relies on nanomaterials with size scales on the order of atoms and molecules, which makes them particularly stealthy when it comes to entering the body. Teamwork is leading to a much-needed standardised system for risk assessment.
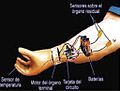
Prosthetic technology has advanced significantly, but complex movement has not yet been realised. EU-funded researchers worked on advancing signal processing, machine learning and pattern recognition to change the status quo for myoelectric systems.

EU-funded researchers have advanced a new generation of sustainable, smart printed products. Integrating paper and electronics they have developed highly functional, printable labels that can reveal temperature, toxicity or pollution levels.

Extracting, processing and manufacturing conventional building materials consume a tremendous amount of energy. Novel biocomposites are reducing that embodied energy and delivering high-performance, eco-friendly materials at no additional cost.

One of the open challenges in science today is to directly observe atomic motions as they occur. Ultrafast electron diffraction (UED) uses electron beams to achieve this goal.

Buildings account for approximately 40 % of total EU energy consumption. An EU project has developed new insulation solutions applicable to façades, wall cavities and interiors to transform buildings constructed before 1975 into energy efficient units, with minimal disruption for occupants.

Europe’s small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the composites business are battling competition from lower labour cost countries. High-performance composites made with low-cost injection moulding should shift the balance in favour of EU SMEs.

The average car uses approximately 40 to 50 square metres of fabric, and not only in its upholstery. Textile fibres are used in seat belts, interior panels, sandwich panels and more, so switching to biopolymers from polyester will make cars much greener.

Strong and lightweight metal and metal alloy components are cornerstones of products in the automotive, wind power and construction sectors. Novel nano-reinforcements and improved casting technologies will enhance product performance and industry sustainability.

Plastics and composites have improved products and applications in numerous industries, from automotive to biomedical to consumer electronics. Smart composite mould technology will advance the state of the art and expand markets for manufacturers.
























