
Low efficiency and high electricity costs pose a barrier to widespread implementation of concentrated solar power (CSP) technology. EU-funded researchers introduced novel concepts in the solar receiver design that facilitate the manufacturing process and decrease costs.

In the future, it should be possible to more efficiently store the Sun's and wind energy thanks to highly conducting ceramic materials.

European researchers are biomimetically designing and 3D printing tissue and organs.

An EU study aimed to reverse the prejudice shown to peoples living around China's borders. Generally seen as undeveloped, the team gave an opposite viewpoint, highlighting historic trade plus modern cross-border relations and economic development.

Achieving better interoperability in rail operation and security is seen as key. An EU initiative addressed various aspects of railway security under one integrated system to help rail operators and security authorities ensure safety for travellers.

EU-funded researchers produced a tuneable laser oscillator that generates signals in the microwave, millimetre-wave and the terahertz (THz) frequency range. This ultra-high frequency oscillator could be a key innovation in the communications sector.

An EU initiative is overhauling the modern factory to make it more productive, more energy efficient and less wasteful – and thus more sustainable.

While light travels at just below 300 million metres per second in a vacuum, EU-funded researchers have investigated the possibility to slow it down and even keep it still.
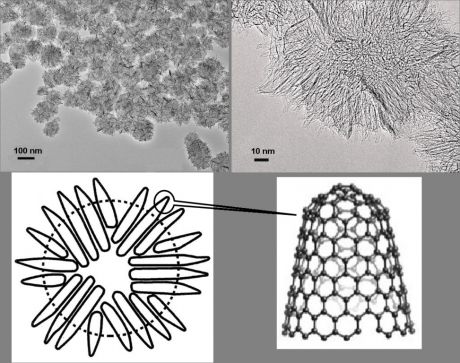
Quantum computation relies on information storage via qubits, or quantum bits. EU-funded scientists are investigating the potential use and physical mechanisms regarding the use of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) for qubit implementation.

An EU-funded research initiative has developed technology that can kill pathogens found on fresh produce. The technology relies on plasma contained inside the packaging to neutralise bacteria.

A consortium of EU research groups and small business has developed improved diets for traditional and modern salmon aquaculture systems.

Solar energy is poised to make a significant contribution to the global energy landscape. Scientists are using the unique properties of tiny semiconducting nanoparticles to increase efficiency, thereby lowering cost and priming the market for widespread uptake and impact.

Manufacturing-grade plastics (also known as reinforced polymer composite materials) are a major industry that is expected to grow exponentially. An EU initiative set out to offset the considerable environmental impacts and negative health effects for workers.

Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) with their high energy densities and fast start-up times are poised to revolutionise the automotive sector. Improved catalysts of the electrochemical reactions could fuel the revolution.

The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at the Franco-Swiss border near Geneva is the largest scientific instrument ever designed and is nearly 30 years in the making. Scientists co-funded by the EU laid the groundwork to significantly boost LHC capacity.
Global positioning systems (GPSs) providing continuous information on worldwide, three-dimensional precise positioning and time has profoundly changed the game for navigation. But what if GPS isn't available?

An EU group devised new approaches to building design that provide full control of a building’s anticipated response to earthquakes. Outcomes include methods for assessing various building types prior to damage and quantifying human factors among consequences.

Chemists are developing new materials with exciting properties by transforming crystalline materials into different structures.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are attracting rapt attention for applications such as hydrogen storage and catalysis. EU-funded scientists successfully measured their electrical properties and elucidated their charge transport mechanism to also promote MOF use as active components in electronic devices.

The furniture industry in Europe has been hit hard by the economic downturn, but opportunities abound despite the challenges. An EU initiative envisions a small-scale factory to manufacture customised furniture products.
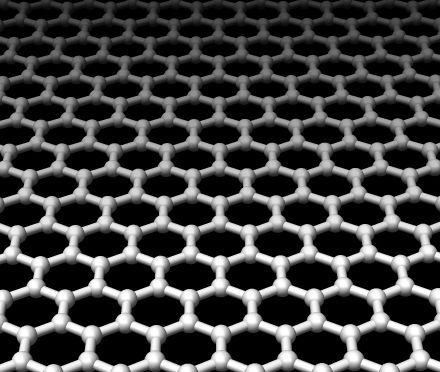
Graphene, a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon, is among the most interesting materials for the production of organic electronics. Scientists are making comprehensive improvements to production methods to significantly lower costs while increasing surface area and quality.

Exploiting the best sustainable urban transport solutions on the planet and promoting knowledge exchange in the field are expected to lead to a better life for European citizens.

Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPVs) are PV modules that can be used to replace conventional building materials in parts of the building envelope, including the façade, roof or window. Important improvements in performance and cost could encourage widespread uptake.

More than a third of all cutting machines among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are turning machines. Adding a third axis to the movement of conventional two-axis machines will have major benefits in terms of time, cost and material usage.

Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) have attracted increasing attention because of their high energy conversion efficiency and lower environmental impact. Some technology limitations could be solved using a modelling approach developed by EU-funded scientists.























