
An EU team developed ways to exploit the wasted capacity in optical fibre networks. Testing of an indoor combined radio/optical system demonstrated speeds up to 5.0 Gb/s.

Bright squeezed vacuum (BSV) light offers huge potential in fields such as microscopic imaging, communication and measurement.

As the world prepares to welcome its first exascale machines, bridging the gap between technical breakthroughs in high performance computing (HPC) and their applications in industrial processes becomes a pressing issue. The NUMEXAS project has developed new numerical methods and computer codes with this objective in mind.

A new turbocharged supercomputer marks a breakthrough in computation capability for a wide range of research applications, from climate change to exploration of the human brain.

A quicker way of gathering and processing input data is destined to result in more efficient equipment for the biomedical field and beyond.

Quantum key distribution (QKD) is an unbreakable form of computer encryption. An EU initiative worked to enable its use among multiple users on public networks.
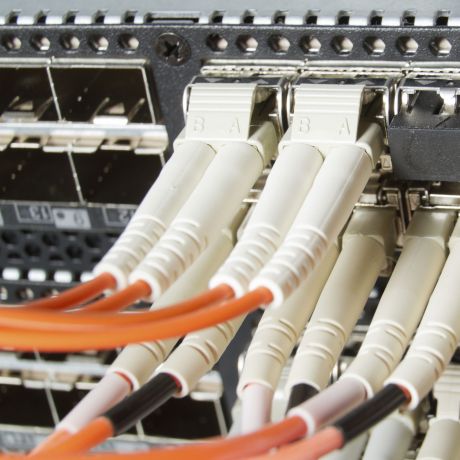

Silicon photonics is an ideal platform for building intelligent transceivers for high-speed fibre optic links. However, lack of suitable light sources close to the chip is the main bottleneck holding back the technology from truly transforming the landscape of telecommunications networks.

An EU team has helped to improve computer recognition of human speech. The work involved introducing to computers large amounts of source materials in a pre-structured format, combined with new algorithms allowing auto-structuring.

EU-funded researchers are reviewing the most recent ideas on how to help people understand why observable events with a scientific basis occur the way they do.

A new generation of expert young researchers in glass and ceramic composites for high-technology applications will ensure a great future for the EU.

Protecting online transactions against hackers often involves a loss of user friendliness. An EU initiative uncovered novel ways to strike a balance between privacy and utility.

More and more geospatial information is becoming integrated into the internet in what has become known as the GeoWeb. An EU initiative helped pave the way to GeoWeb 2.0.

Supercomputers are powerful research tools, but access to these high-performance machines is not open to everyone in the scientific community. An EU initiative provided hundreds of researchers with access to the latest state-of-the-art supercomputing facilities.
As society increasingly relies on high-quality software, applications need to be as adaptive as possible. EU-funded researchers successfully contributed to the development of sophisticated software systems that can readily adapt in the face of changing user needs and environments.

Integrating provenance-based probabilistic information into the Semantic Web can help revolutionise how digital material can be stored and retrieved.

Creating the illusion of depth, stereoscopy offers exciting potential for information visualisation and engaging 3D interactive experiences. An EU-funded project pioneered research on 3D interaction that has hitherto received scant attention.

An EU initiative gathered European researchers to build an advanced digital information space. They offer small businesses the opportunity to better access and leverage online user-generated content.

Fibre optic communication and wireless communication are joining forces to create the next generation of data transfer with faster speeds and enhanced efficiency.

With wireless networks connecting users to information technology devices and to other users, how far behind are wireless interconnects for chips?

Studying the economics of open-source software (OSS) and how it could supersede proprietary software could help Europe innovate while offering cost-effective solutions to users.

With the help of a common collaborative and information sharing platform using the internet, organised crime can be better detected and prevented.

New techniques and coding theories in information sciences are helping to create faster and better data storage.

An EU venture established a school offering training in matters affecting data centres. The team defined training needs while also yielding a community communications portal, new funding relationships, plus novel professional standards.
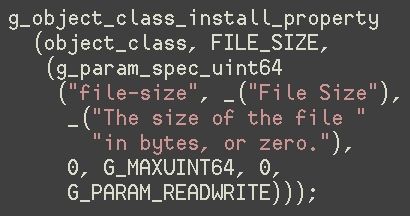
High-tech tools to evaluate applications in software engineering are supporting the use of cutting-edge programming languages that are poised to facilitate software development.

Error propagation is a common feature of every complex network. EU-funded scientists studied this phenomenon to understand how information spreads over networks, knowledge that may lead to improvements in their performance.























