EU-funded researchers are combining high-performance computational power with hardware and servers in order to build a more efficient, heterogeneous cloud.
Businesses looking to cut costs and reduce their carbon footprint now have access to a new tool that evaluates the energy performance of data centres.
With the use of affordable, low-tech femtocells, the EU-funded TUCAN3G project is bringing 3G connection to the otherwise unconnected regions of the world.
To address the evolving cybersecurity threat, the EU-funded SHARCS and PQCRYPTO projects are developing the security paradigms, architectures and software needed to ensure our ICT systems are secure and trustworthy.
What can software designers and ICT specialists learn from maggots? Quite a lot, it would appear. Through understanding how complex learning processes in simple organisms work, EU-funded scientists hope to usher in an era of self-learning robots and predictive computing.
EU-funded researchers have unveiled a set of tools that will make computer systems more energy efficient, providing large data streaming aggregations 54 times more efficient than standard implementations.
Netflix is the undisputed champion of Internet video providers but has never actually had to build its own datacentres. So it hardly comes as a surprise to see engineers across the world craving to find out how the company can withstand such traffic whilst avoiding video stalling during playback. The ENDEAVOUR project team has made this dream come true by finding out how these servers work - and from where.
A team of US and Israeli researchers, partly funded by the EU, have developed a truly pioneering cinema screen that can show 3D films without the need for glasses.
A ground breaking EU project has delivered a cloud-based platform along with a range of apps and tools to help get European cities moving sustainably.
The REPARA project has developed and registered new technologies that are expected to make parallel computing applications more energy efficient, less expensive, and easier to develop and maintain.
EU researchers believe these new, innovative qubits could serve as the information units for the quantum computers of the future.
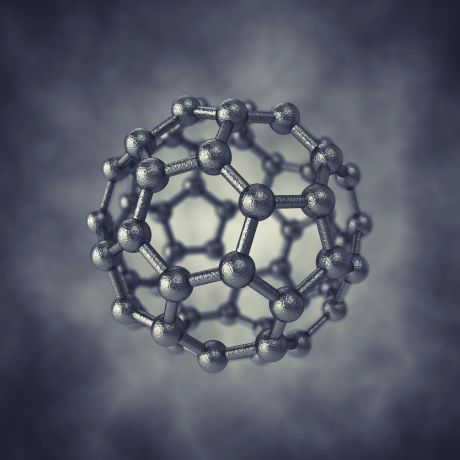
Quantum computation relies on information storage via qubits, or quantum bits. EU-funded scientists are investigating the potential use and physical mechanisms regarding the use of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) for qubit implementation.

Optimal control is a mathematical tool that can be applied to many fields, such as avionics by optimising rocket trajectories, the automotive industry by minimising collision impact, and telecoms to establish a satellite optimal position. An EU initiative provided theoretical and practical training in this field to young mathematicians and engineers.

Studying the economics of open-source software and how it could supersede proprietary software could help Europe innovate while offering cost-effective solutions to users.

The changing nature of jobs and job skills calls for proficiency in digital competencies, critical thinking, flexibility and teamwork. To take on the challenges of a global economy, a newly developed smartphone application can equip employees of the future with these skills they need.

An EU team developed ways to exploit the wasted capacity in optical fibre networks. Testing of an indoor combined radio/optical system demonstrated speeds up to 5.0 Gb/s.

Bright squeezed vacuum (BSV) light offers huge potential in fields such as microscopic imaging, communication and measurement.

As the world prepares to welcome its first exascale machines, bridging the gap between technical breakthroughs in high performance computing (HPC) and their applications in industrial processes becomes a pressing issue. The NUMEXAS project has developed new numerical methods and computer codes with this objective in mind.

A new turbocharged supercomputer marks a breakthrough in computation capability for a wide range of research applications, from climate change to exploration of the human brain.

A quicker way of gathering and processing input data is destined to result in more efficient equipment for the biomedical field and beyond.

Quantum key distribution (QKD) is an unbreakable form of computer encryption. An EU initiative worked to enable its use among multiple users on public networks.

Silicon photonics is an ideal platform for building intelligent transceivers for high-speed fibre optic links. However, lack of suitable light sources close to the chip is the main bottleneck holding back the technology from truly transforming the landscape of telecommunications networks.

An EU team has helped to improve computer recognition of human speech. The work involved introducing to computers large amounts of source materials in a pre-structured format, combined with new algorithms allowing auto-structuring.

EU-funded researchers are reviewing the most recent ideas on how to help people understand why observable events with a scientific basis occur the way they do.

A new generation of expert young researchers in glass and ceramic composites for high-technology applications will ensure a great future for the EU.












