
Transcription is the first step in transformation of the DNA code into actual molecules. Nature has equipped DNA with a system of checks and balances to ensure that transcription is well-regulated, and scientists are elucidating relevant structures.

Researchers are studying a new type of chromosome to better understand how it influences speciation and evolution.
Researchers are revealing key areas for improvement in the manufacture of bioproducts.

A European research team used zebrafish as a model organism to investigate how neurons develop with a specialised cover known as myelin.

Trypanosomiasis, also known as African sleeping sickness, is a fatal infection caused by the parasite Trypanosoma brucei. A European study investigated how Trypanosoma brucei evades immune attack.

The circadian or body clock is a 24-hour cycle that regulates various physiological processes. Understanding how circadian oscillations extend to metabolism was the subject of a European study.

Scientists studied traditionally Arctic-breeding geese that managed to reproduce successfully in new temperate regions. They investigated physiological trade-offs that the geese make to thrive in Arctic vs. temperate Central Europe habitats.

Phytoplankton form the basis of the oceanic food web and sustain themselves using sunlight for photosynthesis and nutrients from the surrounding water. However, a rapid increase in phytoplankton can result in harmful algal blooms (HABs) that release toxins into the marine environment.

A recent research project has investigated whether invasive fish species can influence native species through pheromone signalling.

AN EU-funded project has studied the genetics of a common fungus to find evidence of speciation driven by environmental changes.

Researchers in Sweden studied interbreeding in flycatchers to better understand how species evolve in real time.

Canadian and European scientists have identified microbes that could be used to protect tree and plant ecosystems from disease and pollution.

Thanks to new research into roots and signalling molecules, scientists are one step closer to understanding plant responses to herbivory.

New research has revealed specific genes and proteins that help trees protect themselves against drought stress.

Researchers have advanced a new method to help map soil microbe networks in great detail.

New research has shed light on the important ecological phenomenon of phytoplankton host–virus interactions.

Smell is an essential sense that allows animals to detect food, predators and mates. The elucidation of the underlying neural functions is critical for understanding smell processing.

Understanding the mechanisms that drive biodiversity and species richness is critical to plant conservation in the face of climate change. However, these mechanisms remain one of biology's great unsolved mysteries.

Researchers in the EU have investigated how symbiotic marine microorganisms work together to harvest gaseous nitrogen into a form they can use.

A new pan-European network of expertise and specialist facilities is set to position the EU as a global leader in marine research.
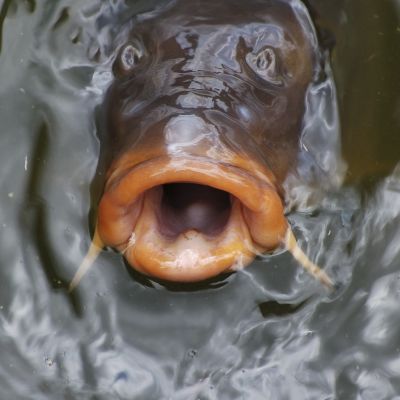

Researchers have advanced our understanding of partial migration in a common fish species.

Researchers in Greece are cultivating and processing microalgae as a source of new chemicals and enzymes for cosmetic products.
A European study investigated the mechanisms by which antibiotic-resistant bacteria evolve. The genetic determinants of this process could have important implications for the spread of microbial resistance.
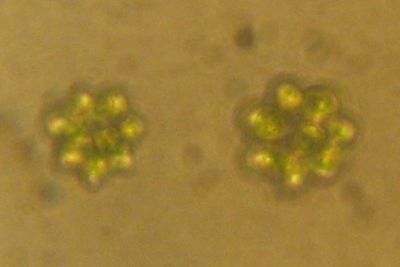
Researchers have studied the genetics of iron metabolism in phytoplankton, comparing a recently discovered microalga with a number of other marine microorganisms.
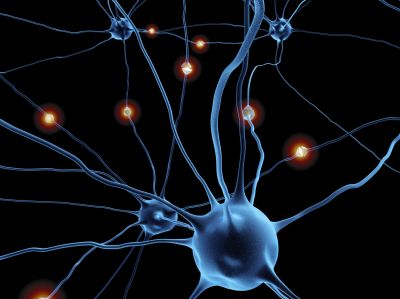
Neuronal cells have strange branching extensions with little knobby bulbs on them called spines, the places where one neuron communicates with another. In pioneering work, scientists have stimulated individual synapses and imaged spine changes.





















