Currently, acute stroke treatment depends on knowing when the symptoms began. A European consortium is working on a method to determine the time window for therapy.
A European consortium is working on new therapies for a group of rare neurodegenerative disorders called Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation (NBIA).

Biofilm-forming microorganisms are a growing problem particularly in healthcare. A European study is looking to address this issue through coating of medical implants with specialised anti-bacterial materials.

Schizophrenia is a debilitating mental illness. EU-funded scientists are developing biomarkers and predictive tests to identify particularly difficult cases early for faster access to the only anti-psychotic that can help.

Researchers have tracked thousands of individual honeybees in a hive to better understand how they communicate and transfer pathogens.
Researchers speculate that the fat surrounding our heart impacts heart biology. A European study set out to understand how this occurs and if it could be exploited for therapy.
In multicellular organisms cells with different fates come from originally uncommitted precursor populations. An EU project investigated the control of cell differentiation in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs).

An EU-funded project has designed the largest genetic study ever of women with pre-eclampsia, and their babies, in central Asia and Europe. Results are expected to deliver a predictive tool for the condition.

European researchers are working on an automated high-throughput method for analysing protein glycosylation. The technology is anticipated to advance current diagnostics and aid the discovery of disease-specific biomarkers.
It seems that the so-called non-coding DNA is not so inactive after all. EU research has uncovered the molecular basis of its involvement in some cancers.
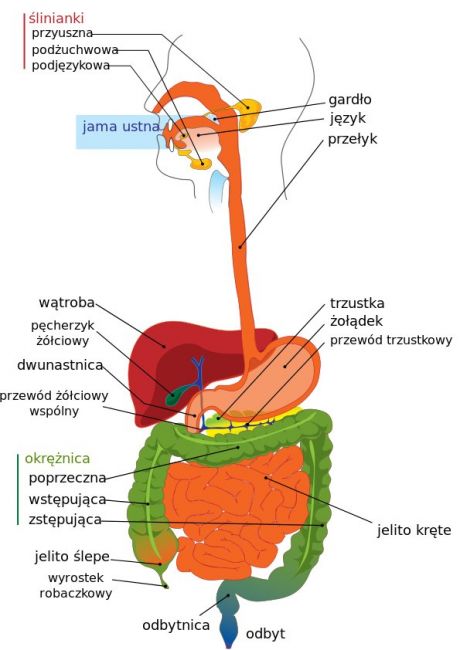
According to the World Health Organisation, it is estimated that in 2005 alone 1.8 million people died from diarrheal diseases. Improved diagnostic tools are thus necessary to act promptly against these dismal statistics.
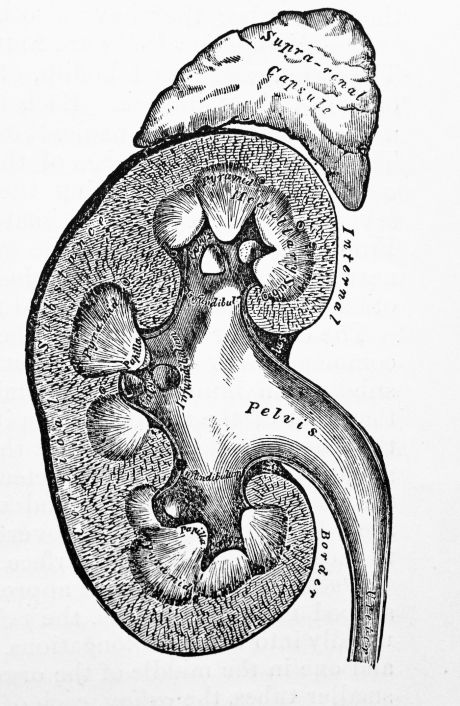
Kidney dysfunction leads to hypertension, which in turn creates more damage to the kidneys. An EU study addressed the mechanisms of salt transport regulation in kidneys using a model system.

The central nervous system works largely on the basis of currents and voltages generated by the flow of ions in or out of neurons. Scientists have shed important light on an intriguing endogenous background electrical activity certain to impact processing of incoming signals.
Currently, no therapy is capable of promoting recovery after complete spinal cord injury (SCI). European scientists developed a brain-spinal interface (BSI) system with a goal to restore movement in severely paralysed subjects.

Researchers are analysing the environmental effects of a growing trend of using recycled organic wastes on arable land as an alternative to landfilling and incineration.

Young EU scientists are investigating new and sustainable ways of utilising the contents of animal waste.

European scientists are working to characterise neural stem cells (NSCs) for cell therapy applications. NSCs possess an inherent capacity to differentiate into different cell types. However the ability of cultured NSCs to produce clinically-relevant neuronal types is gradually lost. To produce clinically-relevant neuronal types, rosette-NSCs (R-NSCs) show promise.
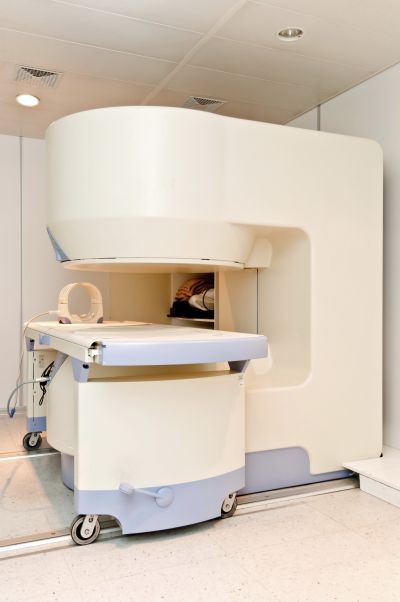
Accuracy in radiation dosimetry and the use of proton/ion beams for cancer therapy are increasing with progress in instrumentation. A large EU training network is conducting cutting-edge research in the development of radiation detectors with a number of industrial and medical applications.
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) have been the backbone of electronics for years. Improved technologies for printed electronics that get rid of the boards and the discrete components will put the EU in a leadership position within a huge global market.
With over 400 000 patients across Europe receiving erythropoietin (EPO)-related treatment every year, it is important to delineate any therapy-associated health hazards. A European study determined EPO-associated risks of tumour growth and thromboembolic events.

Scientists have investigated how the roots of crops respond to periods of flooding in order to ensure good harvests.
EU-funded scientists are developing new organic/inorganic materials that are excellent candidate elements for non-volatile memories. Being both electrically and optically addressed, they pave the way for converging electronic and photonic integrated circuits.

An EU project has developed a number of new diagnostic tests for animal pathogens to improve disease diagnosis at the point of care.
An unprecedented effort has been made to coordinate storage and access to virus collections on a global scale. EU funding has supported the development of a readily accessible virus archive with an extensive collection through global networking.

For any disease, treatment should present minimal adverse effects and maximum therapeutic outcome. To achieve this, a European study is working on genomic biomarkers that predict treatment response in epilepsy.
























