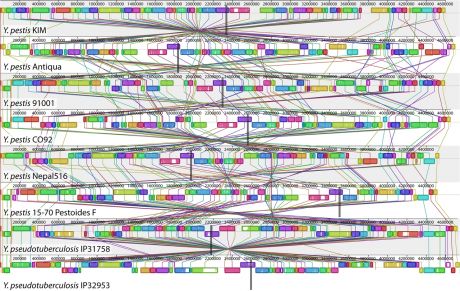
The global research community has dedicated a great deal of time and money to deciphering the human genome. An EU-funded project has applied the knowledge and tools gained in this effort to the life sciences beyond Homo sapiens.

In response to injury, skeletal muscle activates orchestrated molecular mechanisms to restore muscle architecture and functionality. Understanding how this process changes in muscular dystrophy is vital for designing novel therapies.
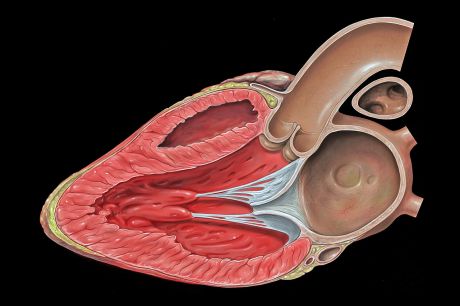
Cardiac arrest remains one of the major challenges of modern cardiology. A European consortium is working on a novel treatment based on ultrasound technology.

The spinner dolphin (Stenella longirostris) contains six groups living in particular habitats (ecotypes). EU funding supported investigation of the evolutionary mechanisms behind the different traits exhibited in these populations.

European researchers studied the process of vascular formation in zebrafish embryos. Their findings bring us a step closer to comprehending this vital process in health and disease.
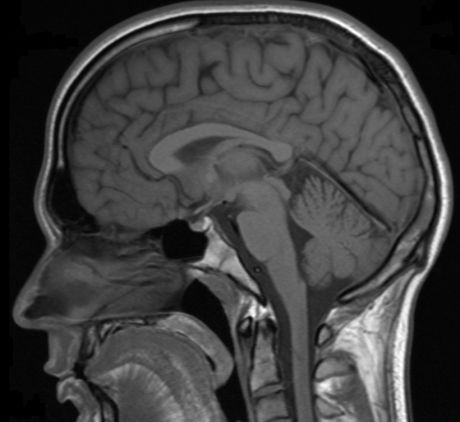
Multidisciplinary research on the workings of the brain and innovations in neuroimaging promise to support the creation of valuable research in addressing neuropsychiatric disorders.

Many fundamental questions about the biology of Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis), such as how they stood and walked, remain unanswered. An EU-funded project studied the bone structure of this extinct human species to reveal the truth.

An EU-funded study is investigating the association between Streptococcus infection and tic disorders. The findings will shed light onto the pathogenesis of tic disorders and determine the genetic and environmental risk factors.

An EU project has taken an interdisciplinary approach to examining the mapping between language and perception across the lifespan of both healthy and clinical populations.

Researchers are using a sparrow hybrid, which recently evolved from a cross between two different sparrow species, to understand the genetics behind speciation.
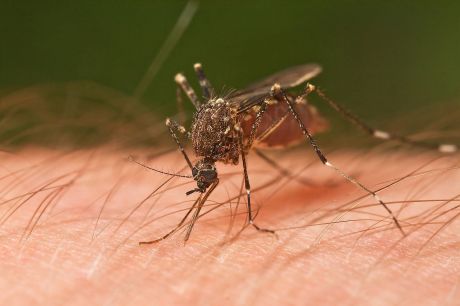
Mosquitoes are carriers (vectors) of a number of infectious diseases, including malaria, dengue and yellow fever – all serious public health threats. A large EU-supported consortium exploited the genetic manipulation of mosquito vectors to control the spread of infectious diseases.

Researchers hope to produce food crops with increased levels of health-boosting carotenoids by finding out how exactly plants regulate production of these high value bioproducts.

Farmers face a constant battle against pests and disease, while climate change may increase their occurrence and severity. The availability of chemical agents to fight plant pathogens is limited to protect the environment and human health; the alternative therefore is to use environmentally friendly sustainable products.

A new EU research initiative is studying the gut microorganisms of more than 1 000 dairy cows to try and limit methane (CH4) and N emissions and improve productivity.

Birds and mammals rely on their sense of hearing to locate prey and escape predators. An EU-funded project set out to explain how sound processing occurs in natural environments.

An EU research project is looking to hemp and flax fibres for creating sustainable packaging.

An interdisciplinary EU-funded initiative successfully addressed crucial questions regarding climate change by analysing different tree ring parameters and applying different statistical approaches.

Recent discoveries relate changes in transfer RNA (tRNA) abundance to apoptosis and gene misregulation in tumourigenic cells. A European study investigated the processes affecting tRNA abundance under stress.
A European study is developing an immunotherapeutic approach based on donor T cells to improve the outcome of haematopoietic cell transplantation. This has direct consequences for the treatment of leukaemia.

An EU consortium comprising companies and research institutes is developing an innovative process for extracting high-value products from microalgae. Its scope extends from feedstock production and harvesting to oil extraction and purification.

An EU project is investigating perennial grasses as a biomass crop that can be grown on marginal land that isn't good for any other use.
Imbalance in mammalian brain development can lead to neurodevelopmental disorders. An EU-funded project is studying cerebral cortex development using a multicolour multi-clonal labelling strategy.
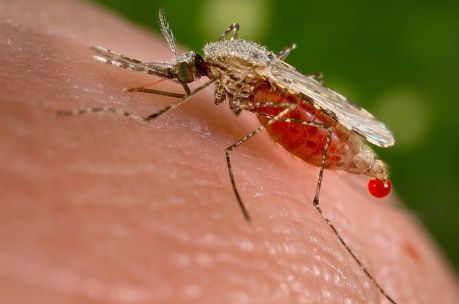
Control of the damaging impact of insects on human health and agriculture mainly involves the use of chemicals. A European study is proposing a more targeted approach, which stems from genomic and biological analysis of vectors.

Producing pharmaceuticals in plants is potentially efficient compared to conventional production methods. Ease of plant engineering and lower production costs could guarantee success for plant-generated vaccines against animal and human diseases.

Understanding the dynamics of microbial communities and the evolution of the antibiotic resistance is critical for devising novel intervention strategies.























