
Like all ecosystems on Earth supporting animal and plant life, aquatic ecosystems need oxygen. However, oxygen availability in these systems is threatened by global warming and excessive input of nutrients such as from agriculture and wastewaters, known as eutrophication.

In the aftermath of the Fukushima nuclear disaster and its effect on the European continent, the EU is seeking to optimise nuclear and radiological preparedness. An EU initiative is developing effective emergency management procedures, methods and tools for such devastating incidents.

Increasing innovation for the exploitation of maritime resources will enable the EU's maritime sector to benefit from global demand for resource-efficient technologies, systems and operations.

One of the most important questions posed by climate change is whether species can respond to a changing climate quickly enough to avoid extinction. In order to survive, populations must either be able to adapt to or tolerate the change in environment, or migrate to more suitable conditions.

An EU team developed new sensors, processing software and models for studying degradation of old buildings. Simulations yielded an accurate assessment of deterioration, considering shape and materials, thus providing conservation prognosis.

An EU team proposed a system for converting vibrational energy into small-scale electrical power. The project proved the device concept, utilising cantilevered PMN-PT layers, while also developing new microtechnology processes.

Europe is considering the viability of a next generation of nuclear energy systems that promise significant advances in sustainability, safety, reliability and costs. An EU initiative aims to deploy one such nuclear reactor prototype in central Europe.

Fluctuations in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) are a major component of the carbon cycle and the climate system. An EU-funded initiative investigated the past role of the Southern Ocean in influencing atmospheric CO2.

Although forests are dynamic systems, the speed of change to which they are subjected is now at an unprecedented level. This is due to factors such as climate change, nitrogen deposition, the introduction of invasive species, and the loss of biodiversity and habitat.

Global climate models that improve the accuracy of seasonal predictions have several limitations. An EU initiative used a large number of climate model simulations to optimise forecasts.
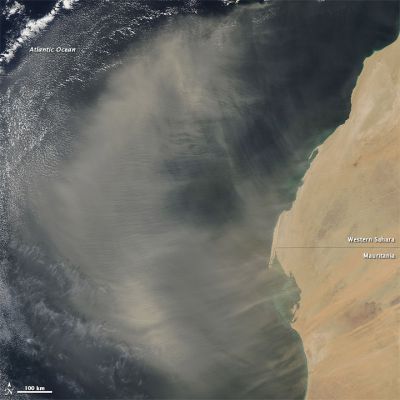

Aside from being a public health hazard, particles in the atmosphere affect climate. New data mining and analysis methods are shedding light on the role of one of the most important components, black carbon.

Researchers have used laboratory experiments to improve our understanding of how radioactive atoms move through clay, contributing to safer radioactive waste disposal.
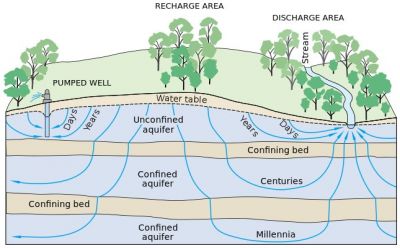
Protection and sustainable use of water supply is one of the most important environmental issues facing humanity. Groundwater is the primary source of drinking water for much of the world, as well as being vital for agriculture and industry, but it is under threat from pollution.
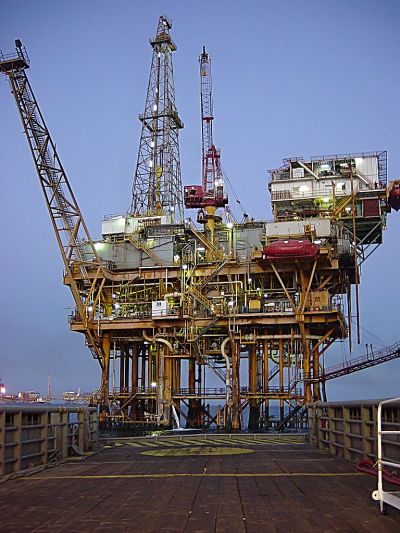

European engineers have developed a self-regulating reversible inflow control device (ICD) to maximise oil production and shut off unwanted water and gas from production wells.

An EU-funded project is working on alternative management pathways for forests with the goal of finding better solutions to the carbon and climate problem.
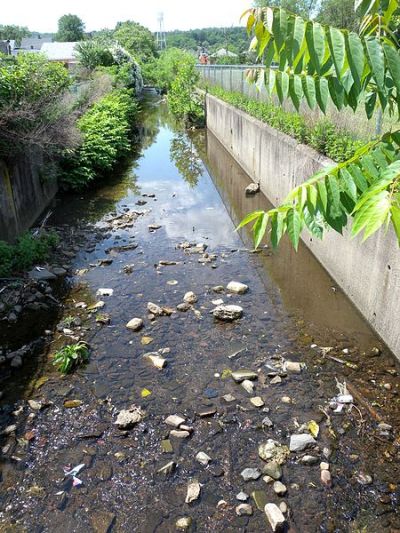

Scientists and engineers are working together as part of an EU-funded initiative to reduce the carbon footprint of wastewater treatment.

Researchers have made progress in understanding how streams and rivers influence global carbon and nitrogen cycles.
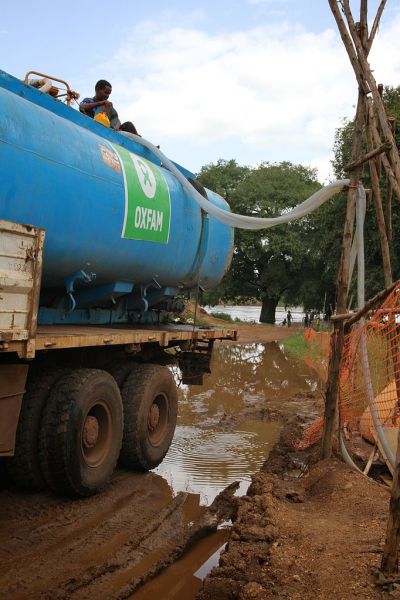

More than a billion people globally do not have enough clean water and 2.6 billion people lack adequate sanitation. Italian researchers in a region challenged by drought plan to remedy that at both the local and global scale.

An EU project improved recycling of agricultural plastics film waste. The group developed a logistics system, also a three-stage process for on-site removal of earth and rocks from the film, involving a dry airflow technology.

Information from a dedicated calibration and validation site has proven invaluable in ensuring the accuracy of satellite altimetry measurements. However, more reliable in situ information can be obtained by an international network being developed within an EU-funded project.

EU partners are developing a toolbox of instruments for use in environmental research in the Danube region. The effort will also benefit stakeholders and the local population.
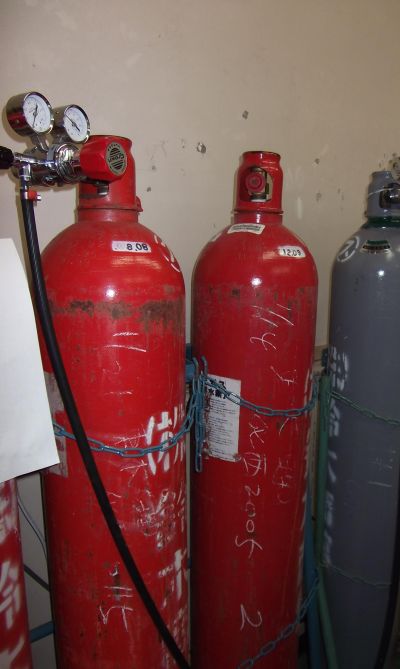

Scientists are developing an integrated bioprocess to produce hydrogen gas (H2) from garden and food waste by fermentation.

Researchers have investigated the use of acoustics technology to clump algal cells together in a concentration step before harvesting them for biofuel production.

Researchers are developing ways to use energy from sunlight for purifying water in remote areas with limited electricity supply.

Hydrogen production from renewable sources is an important step toward reducing carbon dioxide emissions. An EU-funded project seeks to improve the process of extracting hydrogen from wet biomass.
























